WHAT IS REVENUE?
Revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods or rendering of services related to the company’s primary operations calculated as the sales price multiplied by the number of units sold. There are companies who also earn revenue from Interest, royalties or other fees. Since Revenue finds the top most position in the Income Statement it is referred to as the “top line” item of the Income Statement. This is in contrast with the Net Income (gross revenue less total expenses) which is referred to as the “bottom line” of the company. Revenue is also referred to as sales or turnover.
Depending upon the accounting method employed by the company, revenue can be calculated in different ways. Two methods of accounting are mostly used by the accountants- Accrual accounting and Cash accounting. Under the Accrual accounting method, sales made on credit from sale of goods and services are also included in the Revenue. In this method, revenue is recognized even though payment is not received for sale of goods or services. If a company uses Accrual accounting method then to check how efficiently a company collects money it owes from its operations, it has to refer to the Cash Flow Statement. On the other hand, under the Cash accounting method any transaction is considered under the head Revenue only when payment is received for the same unlike the accrual accounting method where revenue is calculated even for credit sales.
We commonly hear of another business term “receipts” in day to day life. There is a difference between receipts and revenue. While receipts are the cash paid to the company, revenue is not necessarily received in cash and may also be in credit. It is possible to have receipts without revenue. If a customer pays cash to the company even before the company has sold goods or delivered services to the customer, it is classified as receipts but not revenue.
Investors often look out for two figures to determine the financial health of the company: Revenue and Earnings per share (EPS). Both the figures are related to each other. A company can increase its EPS by either increasing the revenue or decreasing the expenses. Keeping the revenue constant, the EPS can be improved by cut costs of the company. However, this practice is often not perceived as a positive signal, since company should increase its EPS by increasing revenue to add value to the investors and to grow in the long term. Both revenue and EPS figures are sought after by the analysts and investors in the companies published quarterly or annual reports and any major changes in either of the two figures can affect the stock price of the company.
TYPES OF REVENUE
Revenue is the amount of money that a company brings in selling goods or rendering services. However, as simple as it may sound, revenue can be of different types depending upon the source of income, or the time of recognition, different segments, or different product types.
Types of Revenue according to timing of recognition:
- Accrued Revenue: Accrued revenue occurs when the company has made a sale but has not yet received the payment for the same. In this case, though the sale is counted as revenue for the period but the company has not yet received payment for the same.
- Unearned Revenue: It is the opposite of Accrued revenue. When a customer has already paid for a product or service before the product or service has been delivered or rendered to the customer, it leads to unearned revenue. This is also known as deferred revenue. For example, if a company has been paid for the renovation activity before it has actually completed it leads to unearned revenue. Since it is a debt owed by the company to its customer it is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet of the company.
Types of Revenue according to Source of revenue:
- Operating Revenue: Income from the company’s core or primary source of revenue is termed as the operating revenue. For example, a company into the car business mainly derives its revenue from sale of branded cars but occasionally it also sells merchandise. The revenue it generates from sale of cars is recognized as operating revenue.
- Non-operating Revenue: Any Income from the company’s non-core business or other than primary source of business is called Non-Operating Revenue. In the above car business example, the revenue from sale of merchandise can be classified as non-operating revenue.
In addition to above, revenue can be classified as Gross Revenue and Net Revenue. Gross revenue is the total revenue generated from all the sources while the Net revenue is the Gross revenue minus any adjustments such as refunds, returns and discounts.
Some companies also subdivide the revenue according to the divisions that generate it. For example, Apple Inc. segregates its revenue as revenue from products and revenue from services on the face of the Income Statement. It the notes section, it further segregates the revenue from products as: revenue from IPhone, Mac, IPad and Wearables, home and accessories. Some companies like Alphabet (Google) report revenue by product category wise and geography (addresses of their customers).
HOW TO CALCULATE REVENUE?
The calculation of revenue varies across different companies, sectors and industries. A retailer may have a different formula than a service company. The general formula for calculation of net revenue is as following:
Net Revenue= (Quantity sold*unit price)- Discounts- Returns- Allowances
In the Revenue calculation the main components are: Quantity sold and the Price per unit. However, the formula is a bit different for service companies. In case of service companies number of service hours is multiplied by the billable service rate and for a retailer number of goods sold is multiplied by the sale price of each good. The above formula has to be applied to each product category where a business has multiple product line and then the net revenue of each product line have to be added together to get the total revenue of the company. For Example, Apple Inc. has revenue from multiple products like IPad, Mac book, IPhone, Wearables etc. The revenue from each category of product has to be added to get the total revenue.
Net revenue above is derived by subtracting some of the components that reduce the effective net revenue of the company like the discount offered or allowances awarded to the customers and sales return. The unit price used in the above formula is before deducting the discount and that’s why discount is subtracted separately. If one uses the unit price after deduction of discount, then discount need not be subtracted separately.
REAL LIFE EXAMPLE OF REVENUE REPORTED BY COMPANIES
Let us first see how Alphabet (Google Inc.) reports its Revenue in the Annual Reports of the company.
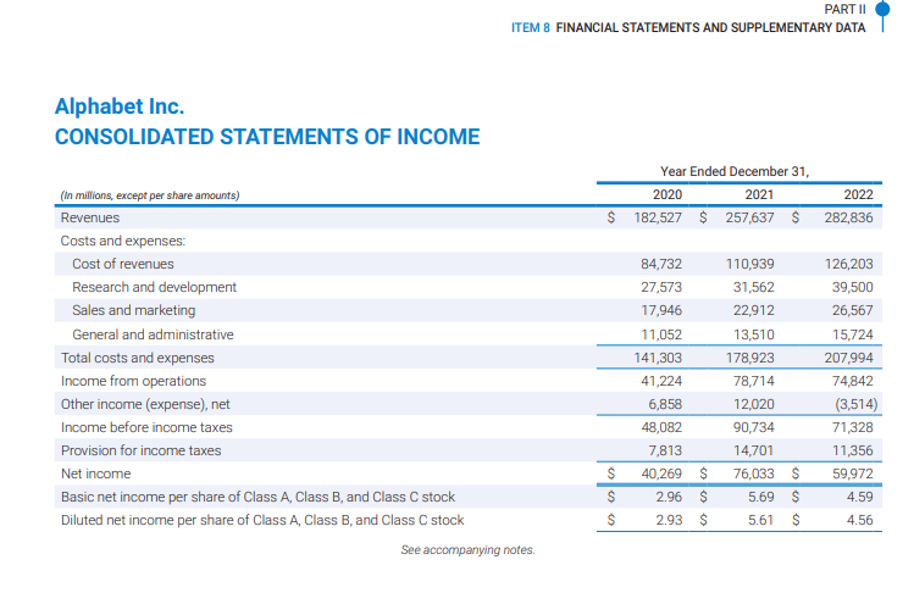
On the face of the consolidated Income Statement, it reports its total revenue. However, when we dig deep into the annual report, we find that in the notes section it provides well explained segregation of its revenue by the type of product or service provided by it and also by the geographical location of its customers.
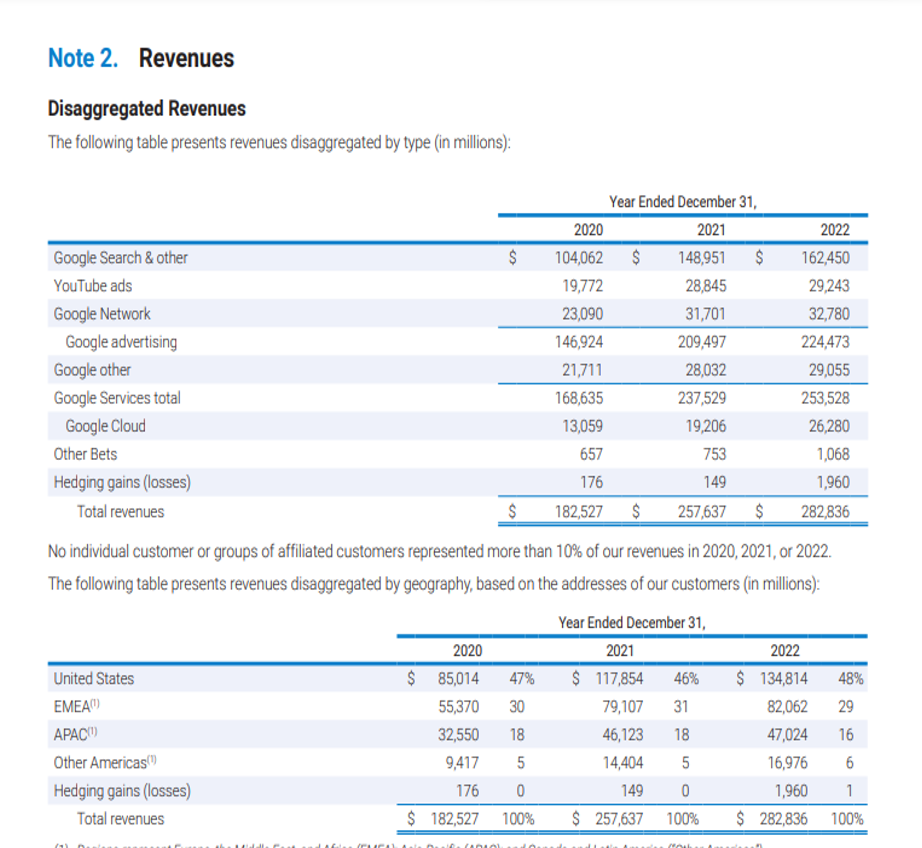
It also has a separate section on revenue recognition from where we can get a detailed idea of what all services or products are supplied by it and from which product and service it derives maximum revenue.


We can look at another example of Apple Inc. which firstly separates its revenue as revenue from products and revenue from services on the face of the consolidated income statement and then in the notes section further provides bifurcation of revenue from different products or services offered by it.
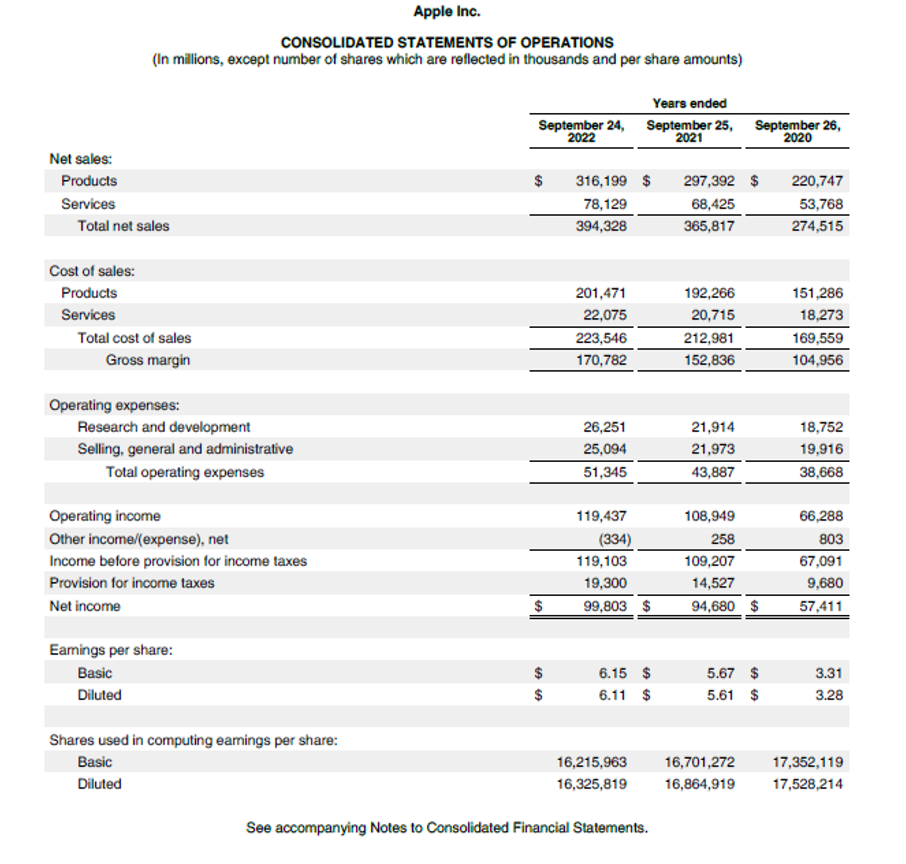
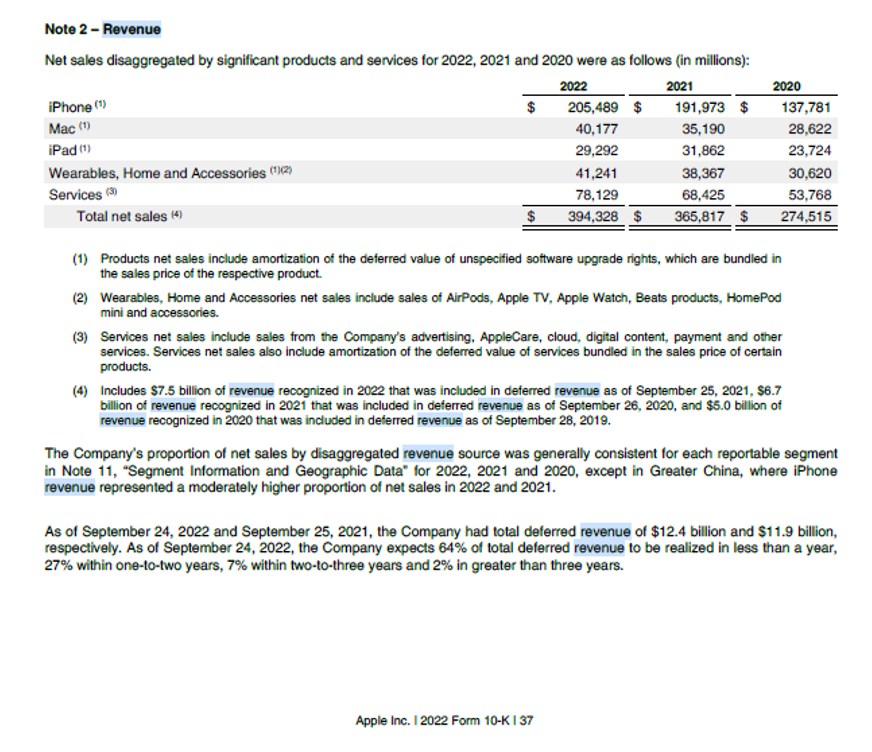
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN REVENUE AND INCOME/PROFIT
Revenue and Income are two of the most used term when referring to the Income Statement of any company. While Revenue represents all the money that a business has earned and incorporates only the income component of an entity’s operations, the term Income incorporates other important components used to run a business. Income is derived by subtracting the revenue from all the expenses important to run any business. These expenses can be the cost of goods sold and other operating expenses or the depreciation, taxes and interest expense. While Revenue represents the gross collection of proceeds, income is the net collection of the proceeds after adjusting for all the expenses. When a company increases its revenue and/or cut down its cost the income increases.
REVENUE RECOGNITION STANDARDS
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the year 2016 released Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606). New guidance on how revenue should be reported by companies is outlined by the accounting standards. The five step guidance requires an entity to recognize revenue as follows:
- First the company should identify its contract with the customers.
- Second the company should identify the performance obligations in the contract.
- Third the company should determine the contract price.
- Forth it should allocate the transaction price to the performance obligation(s) identified in the contract.
- Finally, it should recognize revenue when the entity satisfies any performance obligation identified above.
General Revenue Recognition Standards as per IFRS and US GAAP
| IFRS | US GAAP |
| Amount of revenue can be measured reliably. | Price is determined or determinable. |
| It is probable that economic benefits associated with the transaction will flow to the entity. | Evidence of arrangement between buyer and seller. |
| Stage of completion of the transaction can be measured reliably. | Product has been delivered or service has been rendered. |
| Transaction costs can also be measured reliably. | Recognize when “realized or realizable and earned”. |
| The entity no longer has any managerial involvement or effective control over the goods sold. | Seller is reasonably sure of collecting money. |
MEANING OF REVENUE FOR DIFFERENT TYPE OF ORGANISATIONS
Revenue means different things for different types of organizations. Let’s discuss some of the organizations meaning of revenue.
- Nonprofit revenue: Revenue for Nonprofit organizations include government grants, membership fees, donations from individuals, foundations, and companies, investments, unsolicited donations or fundraising events.
- Government Revenue: The government collect revenue in the form of fees, fines, taxation, sale of securities, sale of minerals or resources right, inter-governmental grants or transfers, collections made from citizens within its district and other government entities.
- Real Estate Revenue: For real estate revenue is generated from flat rent or parking fees.
REVENUE USED TO CALCULATE VARIOS FINANCIAL METRICS
Since revenue is the key figure in the financial statements for investors and analysts, it is used to calculate various financial metrics important to take investment related decisions and make inter-company comparisons. Some common ratios that use revenue figure in its calculation are as follows:
- Return on Sales Ratios
- Gross Profit Margin: Financial metric used to assess a company’s financial health and business model by revealing the proportion of money left over from revenues. Higher margin means company has competitive advantage in product costs.
Formula
Gross Profit Margin= Gross Profit/Revenue*100
- Pretax Margin: It is a company’s earnings before tax as a percentage of total sales or revenues. Higher the margin, more profitable the Company is.
Formula
Pretax Margin= Pretax Profit/ Revenue*100
- Net Profit Margin: It is the percentage of profit from business operations after deducting business operating expenses, interest expense, taxes and preferred stock dividends from revenues.
Formula
Net Profit Margin= Net Profit/ Revenue*100
- Operating Profit Margin: It is a measurement of what proportion of a company’s revenue is left over after paying for variable costs of production such as wages, raw materials, etc.
Formula
Operating Profit Margin= Operating Profit/Revenue*100
- Activity Ratios
- Receivables turnover: It shows time between a sale and cash collection. High turnover (low DSO) means highly efficient credit and collection or strict credit policies.
Formula
Receivables Turnover= Annual sales/average receivables
- Total Asset Turnover: It is the company’s ability to generate revenues with a given level of assets. A low ratio maybe due to inefficiency or of relative capital intensity of the business.
Formula
Total Asset Turnover= Revenue/Average Total Assets
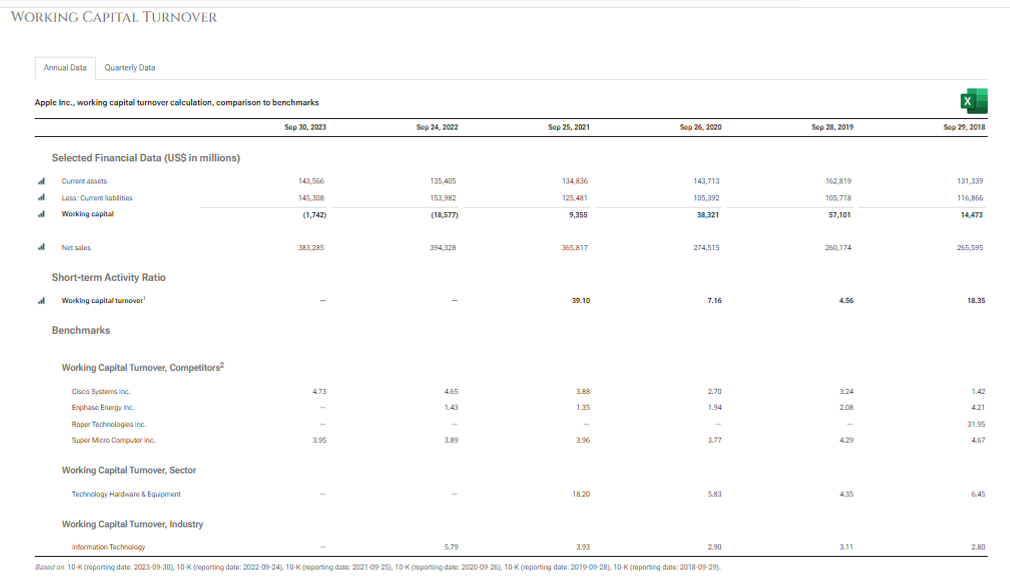
- Working Capital Turnover: It shows how efficiently the company generates revenue with working capital.
Formula
Working Capital Turnover= Revenue/ Average Working Capital
REAL LIFE EXAMPLE OF RETURN ON SALES RATIO CALCULATION
Let us see example of Return on sales ratio calculation for Apple Inc. and compare the ratios with its competitors.
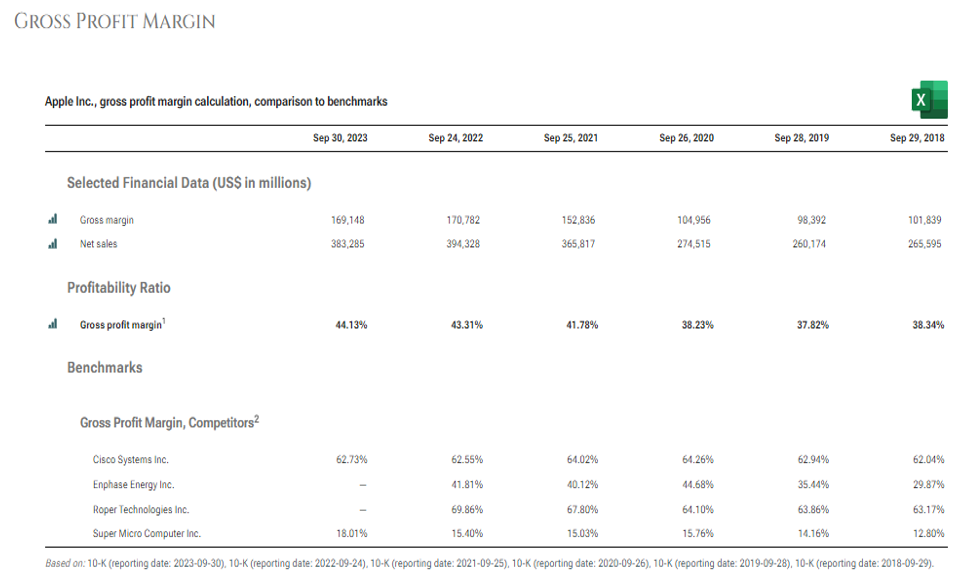
Source: https://www.stock-analysis-on.net/NASDAQ/Company/Apple-Inc/Ratios/Profitability
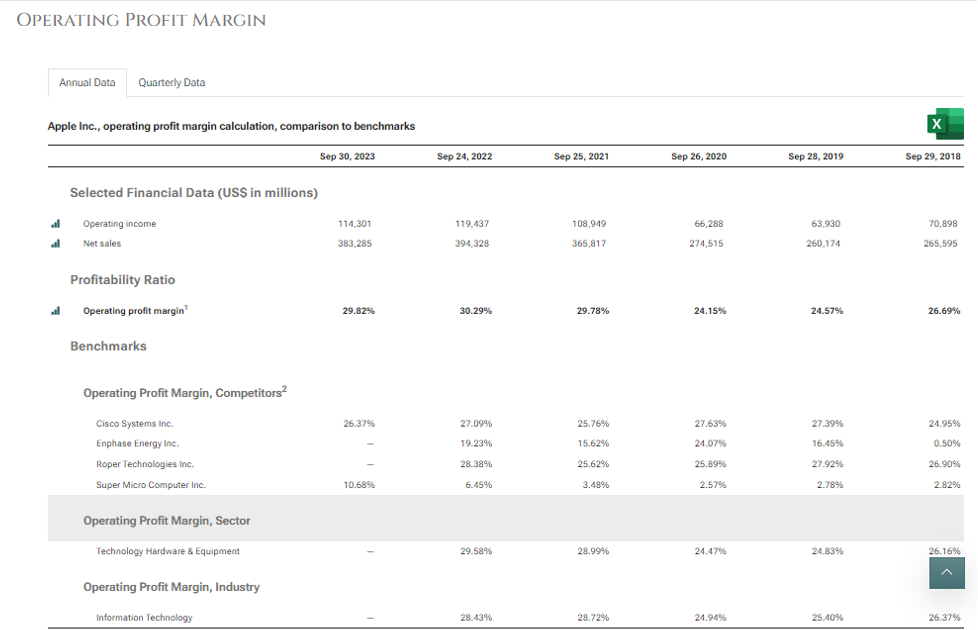
Source: https://www.stock-analysis-on.net/NASDAQ/Company/Apple-Inc/Ratios/Profitability
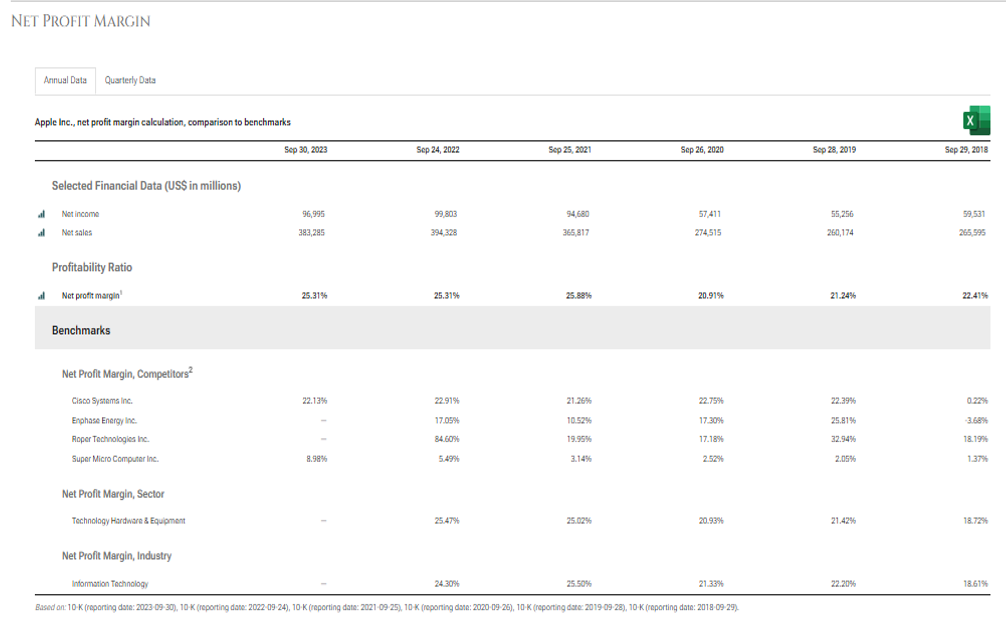
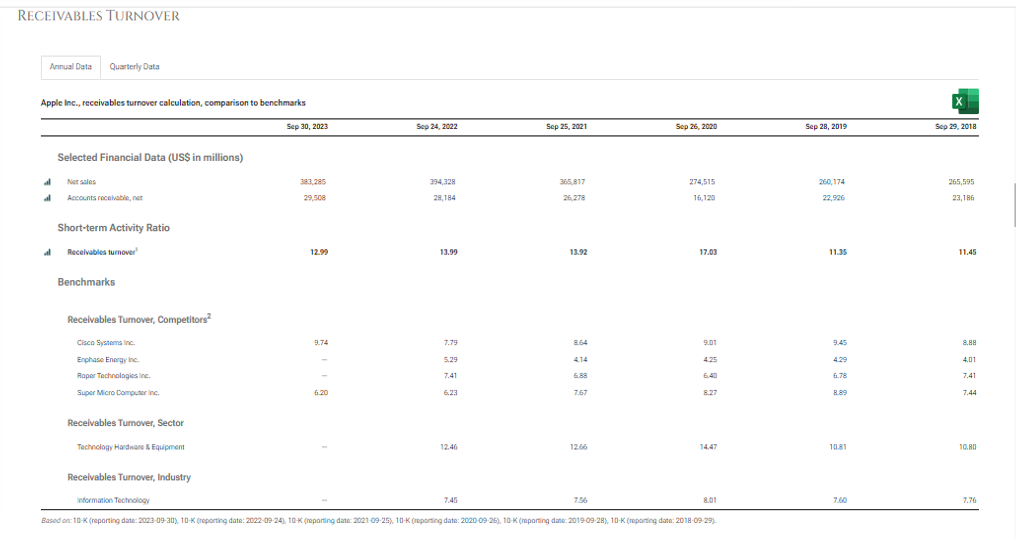
Read more about this post on our LinkedIn page:



3 thoughts on “Revenue – the top line that everyone is chasing”
[…] can be a positive or negative value. A positive EBITA shows that the company is generating more revenue from its operations than the expenses it incurs on carrying out its operations. It shows that after […]
[…] Gross Profit Margin: The gross profit margin indicates the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It measures a company’s ability to […]
[…] enterprise value, factors such as the company’s revenue growth, profitability, cash flow generation, and capital structure can have a significant impact. […]
Comments are closed.