WHAT IS PROFIT MARGIN?
A profit margin in accounting and finance relates to a measure of a company’s profit or earnings relative to its revenue. It is the most straightforward and commonly used measure of profitability of a company. The profit margin shows how much a company makes per dollar of revenue generated and are typically expressed as percentage. For example, if a company has 70% profit margin, it means that a company has made $0.70 of profit for every dollar of revenue generated. The margin represents the profit that a company gets to keep out of its revenue after subtracting all of its costs.
Profit margins can either be positive or negative. Negative margins may indicate that the company is either struggling to manage its cost or not making enough revenue to generate profit. The ultimate goal of the companies is to maximize their profit margins by either cutting cost or by increasing their revenue.
Profit margins are used widely by management, investors and analysts to make profitability comparison of different companies in the same sector and over a period of time. Simply looking at the Net profit or gross profit of any company on a standalone basis will do no good as the comparison base is missing. These margins become more useful only when used to compare with the margins of other companies within the same industry or used for year on year analysis of a company’s financial performance. These margins may not be relevant if compared for different types of industries as what is a good or bad profit margin varies from one industry to another.
While business of all the scale, from a local retailer to a large scale manufacturer calculates the profit margin at their own desired frequency but most of the large publicly traded companies are required to report these margins in accordance with the standard reporting timeframes like quarterly or annually.
TYPES OF PROFIT MARGIN
There are commonly four types of profit margins calculated by most of the business, out of which the net profit margin is the most famous and commonly used as this margin takes into account the bottom line item of the income statement and is the ultimate measure of a company’s profitability after accounting for all types of expenses and taxes. Important to point out that the data for calculating the profit margin of any company is reported completely in the Income Statement of the company.
All these 4 types of margins are discussed below:
- Gross Profit Margin: Any business reports revenue as the first item in its income statement. To earn this revenue, it incurs some direct cost of procuring the products and services. Gross profit is nothing but the revenue minus direct cost of goods or services. This gross profit is divided by the total revenue and multiplied by 100, giving us the Gross profit margin. The gross profit margin can be used by management to identify successful vs. unsuccessful product or service lines where the business has multiple product or service lines. This margin shows which product or service generates the highest gross profit as compared to revenue.
Formula: Gross Profit Margin= (Net Sales-Cost of goods sold)/Revenue*100
Where,
- Net sales (also referred to as revenue less any discounts, taxes, returns) — it is the amount of money generated from selling products, goods, or rendering of services.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS)- it is the raw materials, labor, manufacturing expenses etc. directly related to generating he revenue.
- Revenue- It is the profits generated from the sale of goods, products, and rendering of services
- Net sales minus Cost of goods sold gives us the gross profits.
- Operating profit margin: After accounting for the direct cost, a company accounts for its indirect cost like those associated with advertising or maintaining company headquarters, research and development cost, depreciation etc., except interest cost and taxes. The Gross profit minus these indirect cost gives us the operating profit. Operating profit is calculated as operating profit divided by the revenue and multiplied by 100. It is a measure between gross profit margin and pre-tax profit margin. This margin is used to determine if a company is managing its operating expenses effectively and to know the percentage of funds available to pay the Internal revenue service and the debt and equity holders of the company. Operating profit is used to compare companies in states that may have different tax rates.
Formula: Operating profit margin= Operating profit/Revenue *100
Where,
- Operating profit- it is revenue minus operating expenses.
- Revenue- It is profits generated from the sale of goods, products, and rendering of services.
- Pre-tax profit margin: From the Operating profit a company deducts interest on debt and adds or deducts any unusual outflows or inflows unrelated to the main operations of the company to give the pre-tax profit. Pre-tax profit margin is calculated as pre-tax profit divided by the revenue and multiplied by 100. It is a measure between Operating profit and Net profit margin.
Formula: Pre-tax profit margin= Pre-tax profit/Revenue *100
Where,
- Pre-tax profit- it is operating profit minus interest on debt and any adjustment (add/less) of unusual charges or inflows unrelated to the main operations of the company.
- Revenue- It is profits generated from the sale of goods, products, and rendering of services.
- Net profit margin: From the pre-tax profit a company deducts taxes giving us the net profit which is he bottom line of the income statement. Net income is derived by deducting all the expenses like cost of goods sold, debts, operating costs, depreciation, interest expenses and taxes from the Revenue. This is the most commonly used margin since it accounts for all the company’s cost both direct and indirect cost.
Formula: Net profit margin= Net profit/Revenue *100
Where,
- Net profit- it is pre-tax profit minus taxes
- Revenue- It is profits generated from the sale of goods, products, and rendering of services.
USES OF PROFIT MARGIN
The Profit margins are widely used by the internal and external stakeholders of the company to make varies decisions and analysis. Let’s discuss them one by one.
- Used to address operational issues and study corporate performance: Profit margins are used by the business owners, management of the company and external consultants like auditors to study the corporate performance of the company at varies levels like operating level or net income level to address the company’s operational issues or its struggle to remain profitable. A negative or zero profit margin means that a company may be struggling to control and manage its expenses or make revenue from sale of goods or rendering of services. Since profit margin gives us the hint of any problem, further drilling its components down give us the idea of where the problem lies like the underutilized employees and other resources or high office rentals or unsold inventory.
- Used to comparison to divert resources to the best product or service: The enterprises operating in multiple divisions, product lines, geographical locations use profit margins to assess the performance of each of such division, product line or location to compare which of these are best or worst performers and accordingly divert the resources to that sector, division or location that reaps maximum profits.
- Used by company to seek funding: Both small and large companies need to compute varies profit margins to seek loan from banks or other financial institutions. Banks study varies ratios the most important being the profit margin to assess whether the company will remain profitable in the long run to pay off its interest and principle payment obligation.
- Used by large companies to raise money: Large companies who plan to issue debt to raise money have to disclose their intended use of capital to provide insights to investors about the profit margins that might be achieved by the company either by cutting down its cost, increasing its revenue or a combination of both. Profit margins are important part of equity valuations for initial public offerings.
- Used by Investors to assess its investment decision in a product/service or compare two or more ventures: Investors use profit margins to make varies investment related decisions. While funding a particular start-up an investor may want to assess the profit margin of the potential product or service being developed and also used to compare two or more ventures to identify the better investment option.
EXAMPLES OF HIGH AND LOW PROFIT MARGIN INDUSTRIES
Generally, the procurer or the manufacturer of a high end accessory or luxury goods have a potential for high profit despite of low sales volume as compared to the producer of a low end product. One of the main reason behind this is that a high end product for example a very costly car is usually not even produced until ordered by the customer making it a low cost process for the producer without needing much operational overhead. Gaming and software industries generally make huge investment in software or video game initially but make huge money later by selling copies with little additional expenses. Similarly, companies that acquire patent rights like phone manufacturing or pharmaceutical companies incur high initial research cost but make huge profits later on when they launch and sell the products in the consumer market. For high margin industries, it is also true that the price the customers are willing to pay is high which may be due to better product quality (i.e. R&D) and/or due to marketing activities like sales promotions, advertisements, etc.
On the other hand, some industries have high operational cost like the transportation business. Such industries have to deal with fluctuation expenses like fuel price, drivers wages and retention cost and vehicle maintenance cost. Due to fluctuating prices they have lower profit margins. Automobile companies also have high operational cost of networking, marketing and logistics and low margins since they face intense market competition and uncertain customer demand. Even the agricultural companies have low profit margins due to its high dependence on weather conditions, high inventory cost, resource intensive activities and high operational activities.
REAL LIFE EXAMPLE OF CALCULATION OF PROFIT MARGIN OF A COMPANY
Let us understand the Profit Margin calculation of Apple Inc. for the last 6 years.
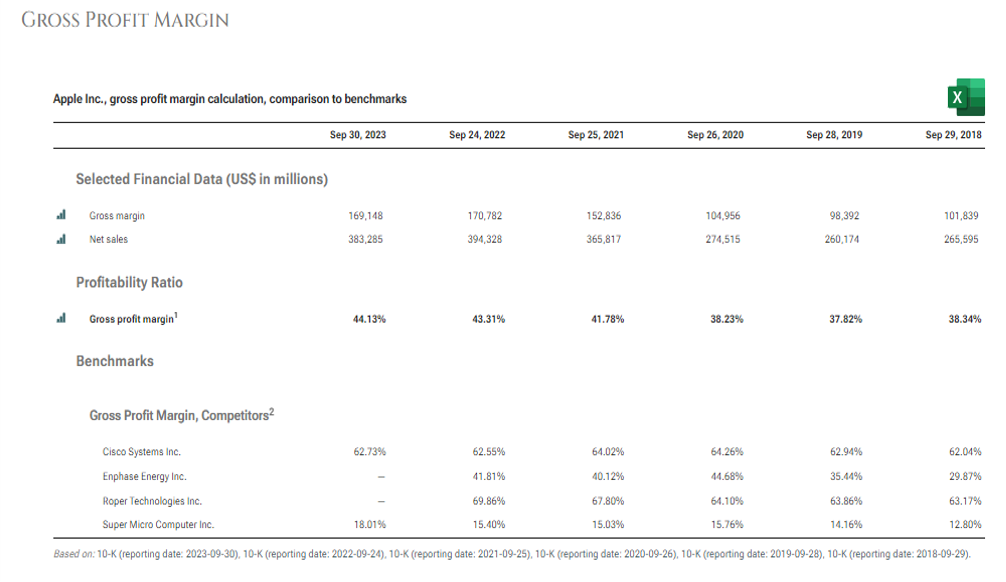
Source: https://www.stock-analysis-on.net/NASDAQ/Company/Apple-Inc/Ratios/Profitability
As we can see above, Gross margins have been increasing year on year for Apple, it has however been lower than Cisco and Roper Technologies in general.
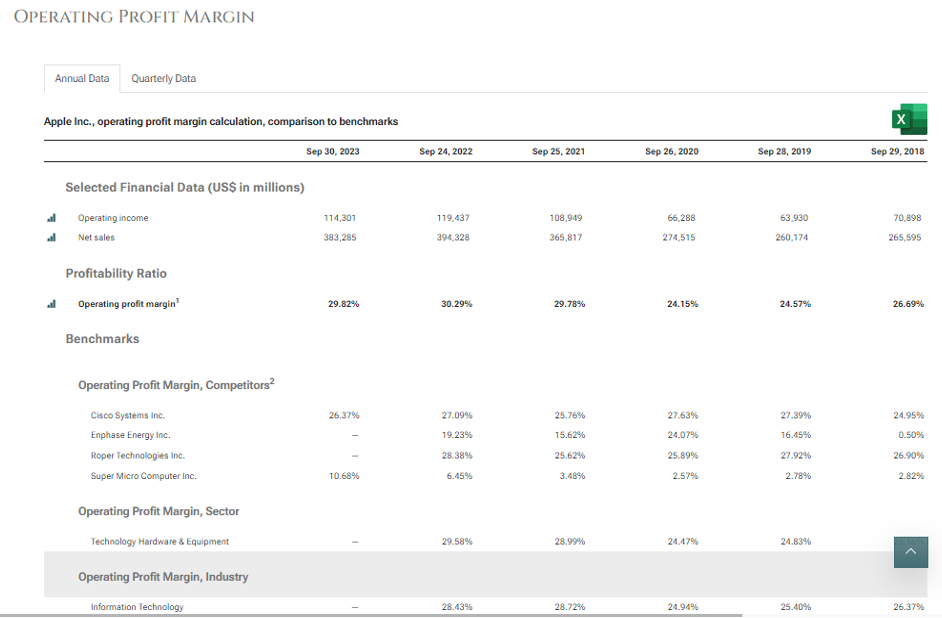
Source: https://www.stock-analysis-on.net/NASDAQ/Company/Apple-Inc/Ratios/Profitability
Apple’s operating profit margin has been higher than the overall Information Technology space in the above sample set.
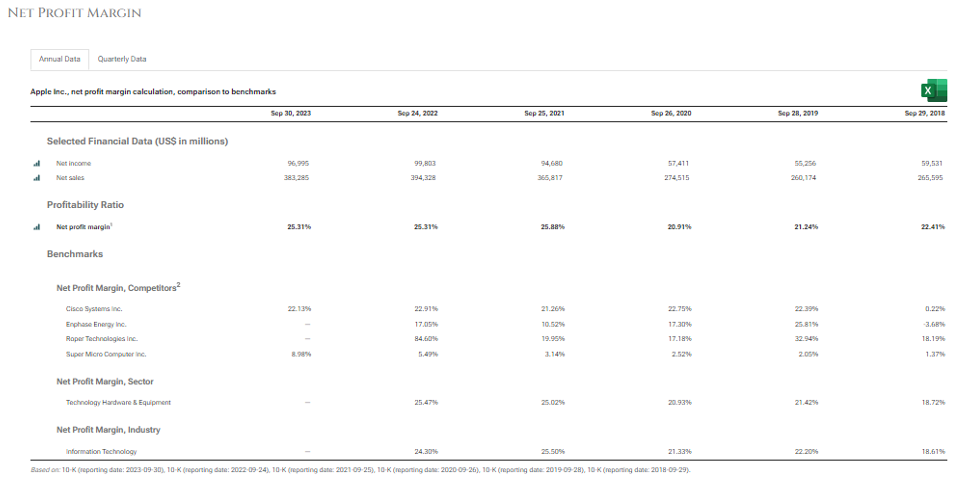
Source: https://www.stock-analysis-on.net/NASDAQ/Company/Apple-Inc/Ratios/Profitability
As we can see, Apple net profit margin has been close to the average of the Information Technology (IT) space.
Overall, Apple is much higher in operating profit margin metrics than compared to the broader IT space and hence is indeed one of the higher profit margin companies globally.


