Introduction
A business, performing its daily operations, generates assets and liabilities over time. The categorisation of assets and liabilities as short-term and long-term depends upon how long the company will record them in its financial statements. In this article, we will try to understand current liabilities, the types of current liabilities, how they differ from non-current liabilities, etc.
What are Current Liabilities?
Current Liabilities are a company’s financial obligations, due within one financial year. The businesses record current liabilities on the balance sheet under the liability column. Current liabilities are short-term because the business services them within one year or an operating cycle. Businesses usually pay off their short-term liabilities using their current assets. Accounts payable, accrued expenses, and other current liabilities like unpaid dividends, income received in advance, etc, are a few examples of current liabilities.
Types of Current Liabilities
A business categorises current liabilities as:
- Accounts Payable is the money owed to creditors and suppliers for the goods purchased on credit. The accounts payable represent the outstanding balance owed to suppliers. By delaying the payment to creditors or suppliers, companies lengthen their cash cycles and boost their cash flows.
- Accrued Expenses are the expenses that are due but not paid. Accrued expenses include tax payable, salaries or wages, interest, rent, utility expenses, etc.
- Other current liabilities include:
- Short-term loans are the funds raised by the company to meet short-term or temporary capital needs. They are payable in 6 months to a year. Examples are payday loans, lines of credit, invoice financing, etc.
- Current Portion of Long-Term Debt (CPLDT): This refers to the amount of long-term liability coming due within the next twelve months. Investors and creditors use CPLDT to understand the liquidity status of the company.
- Unearned revenue, also known as advance payments or deferred revenue, refers to the payments received in advance for goods or services that are yet to be provided. These revenues are to be settled and recognised as earned within a year.
Accounting of Current Liabilities
The accounting of current liabilities involves recognition, recording and management. The first step in the accounting of the current liabilities is recognition. The business needs to acknowledge and measure its obligations, payable in the financial year.
The next step in accounting is the recording of current liabilities. Businesses record current liabilities in the balance sheet under liabilities. Current assets or the revenue generated by operating activities are generally accountable for paying off the current liabilities.
The last step in the accounting procedure is the management of current liabilities. It is a vital step which ensures the liquidity of the business. A practical current liability management system helps companies avoid short-term financial crunches. Firms use strategies like negotiating payment terms with supplies, inventory management, monitoring cash flows, factoring, etc, to manage their current liabilities.
Real Life Example of Current Liabilities – Exxon Mobil
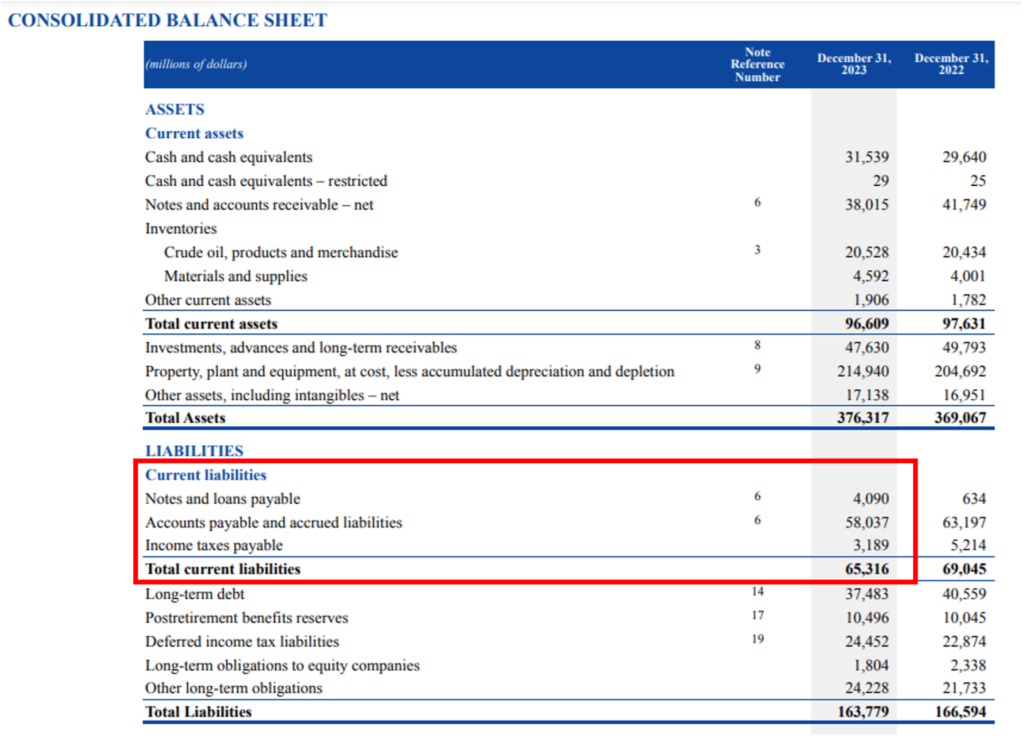
We will understand the current liabilities of Exxon Mobil for 2023:
The current liabilities of Exxon Mobil for 2023 totalled $ 65,316 million. Exxon Mobil has recorded three-line items in the balance sheet under current liabilities, they are notes & loans payable, accounts payable & accrued liabilities and income tax payable.
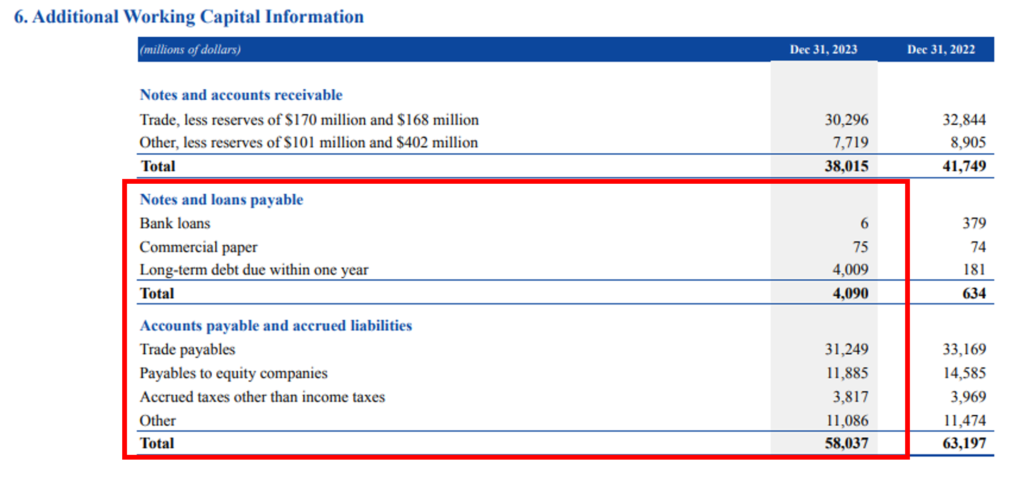
The company has shown an in-depth breakdown of current liabilities in the notes: 6 Additional working capital information page 90 of the annual report.
Here, the company showed that it has raised short-term capital of $6 million and $75 million from bank loans and commercial paper respectively. Under notes & loans company has also recorded the long-term debt which is payable in 2023 of $4,099 million.
Under accounts payable & accrued liabilities Exxon Mobil has noted trade payables of $31,249 million. Trade payables form the biggest expense of the current liabilities in 2023. The company has also recorded payables to equity companies, accrued tax expenses and others with $11,885 million, 3,817 million and 11,086 million respectively.
5-Year Analysis of Current Liabilities of Exxon Mobil
To get a better understanding of current liabilities and their management we will now see a 5-year analysis of current liabilities from 2019 to 2023.
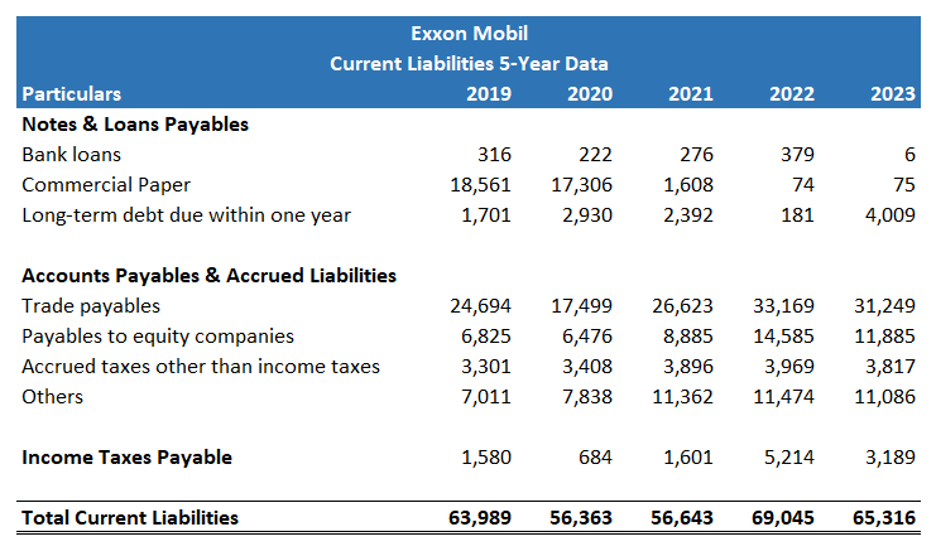
Figures in USD Millions
Note: The data for the 5-year trend analysis is taken from the annual report of Exxon Mobil. The source to access the 10-K reports is as follows.
Source: https://investor.exxonmobil.com/sec-filings/all-sec-filings?form_type=10-K&year=
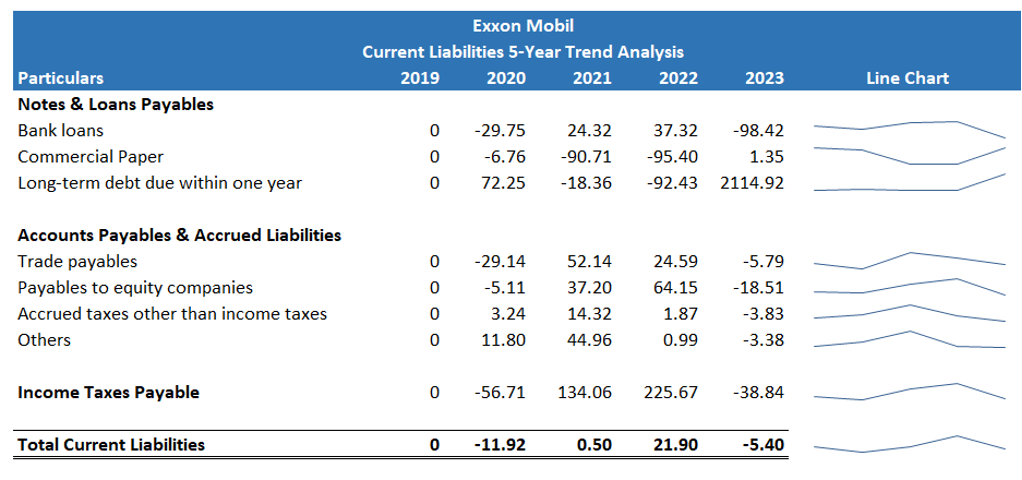
Figures in percentages (%).
For the trend analysis, we have calculated the percentage change that the line item experienced when compared to the previous year’s value.
The positive values show a percentage increase in the value of the line item, and the negative values show a percentage decrease in the figures of the line items compared to the previous year.
- Over the year, Exxon Mobil has raised short-term funds from bank loans, but in 2023, a significant drop of 98.4% in the bank loan is visible.
- Similar to bank loans, commercial paper experienced a sudden dip of 90 and 95 per cent in 2021 and 2022, respectively. Exxon Mobil raised short-term funds from commercial paper in 2023.
- Exxon Mobil has serviced a significant amount of long-term debt in 2020, 2021 and 2023.
- Trade payables form a big part of current liabilities. In 2020, Exxon Mobil paid off trade payables. Then for the next two years, the company increased the credit acquisition.
- Similar to trade payables, the values of payables to equity companies in 2021 and 2022 increased by 37 and 64 per cent, respectively.
- Accrued taxes other than income taxes and others experienced an increase from 2019 to 2022.
- Income Taxes Payable were prominent in 2022 and 2023.
Difference Between Current and Non-current Liabilities
Current liabilities, also called short-term debts and obligations, are financial obligations settled within a year or an operating cycle. The non-current liabilities are the long-term debt obligations that are due in more than one year.
Current liabilities include accounts payables, accrued expenses, commercial papers, etc. Non-current liabilities workaround long-term loans, bonds payable, long-term debts, debt repayment, deferred payments, etc.
Maintenance of current liabilities is crucial for stabilising liquidity and for short-term solvency. Higher levels of current liabilities can cause liquidity issues or financial distress. Non-current liabilities show the leverage and long-term growth opportunities of a business. Higher leverage increases financial risk and exerts a long-term burden of debt repayment on the firm.
Relationship of Current Liabilities and Current Assets
The current ratio helps us see the relationship between current assets and current liabilities. It measures the company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations using its current assets.
The current ratio, the working capital ratio, divides current assets by current liabilities to measure the company’s financial health. It also measures the company’s ability to pay off its short-term debt obligations.
| Current Ratio | = Current Assets/ Current Liabilities |
Calculation of the Current Ratio of Exxon Mobil for 2023:
| Current Assets | = 96,609 |
| Current Liabilities | = 65,316 |
| Current Ratio | = Current Assets/ Current Liabilities |
| = 96,609/ 65,316 | |
| Current Ratio | = 1.47 |
The current ratio of Exxon Mobil for 2023 was 1.47. This means that current assets are 1.47 times more than the company’s current liabilities.
Summing Up
Current liabilities play a crucial role in assessing a company’s short-term financial obligations and overall liquidity. Understanding the types and management of current liabilities is essential for maintaining financial stability and avoiding liquidity crises. While current liabilities are settled within a year or an operating cycle, non-current liabilities reflect long-term debt obligations and leverage. Businesses can ensure their short-term solvency and support sustainable growth by effectively managing current liabilities and maintaining a healthy current ratio. Thus, a proper balance between current assets and current liabilities is vital for achieving financial stability and success in a dynamic business environment.


