Beta analysis measures how a company’s stock moves relative to the overall market, revealing its level of volatility and systematic risk—the risk tied to the broader market that cannot be eliminated through diversification. For example, companies like Apple, with its tech dominance, have a beta close to 1, meaning their stock moves in line with market benchmarks like the S&P 500. In contrast, Tesla’s beta is often above 1, indicating higher volatility and greater exposure to systematic risk. On the other hand, a gold company like Barrick Gold typically has a beta below 1, as gold prices often rise when markets, like the S&P 500, fall. Meanwhile, consumer goods companies like Procter & Gamble have lower betas, reflecting their stable demand and lower volatility in turbulent times.
Beta analysis is a critical tool for assessing a stock’s exposure to systematic risk, forming a key part of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). Let’s see what different beta means:
- β =1 suggests the stock moves with the market, such as the S&P 500,
- β > 1 signals higher volatility compared to the market.
- β <1 but >0 shows lower volatility compared to the market .
- β =0 like for some utility companies, show no connection to the market.
- Negative β like gold stocks, move opposite to the market, acting as a hedge during downturns.
WHAT IS EQUITY BETA AND ASSET BETA ANALYSIS?
Equity Beta and Asset Beta analysis are essential metrics that help investors understand different dimensions of risk associated with a company’s stock. Equity Beta, often referred to as levered beta, measures how a company’s stock volatility compares to the broader market, taking into account its capital structure and financial leverage. For instance, if Tesla has an equity beta of 1.6, this indicates that its returns are expected to be 160% as volatile as the market, reflecting how sensitive the stock is to macroeconomic fluctuations. This metric is crucial for investors, as it illustrates the increased risk that comes from the company’s debt obligations; higher leverage means more earnings are dedicated to servicing that debt, which can amplify stock volatility. When looking up a company’s beta on platforms like Bloomberg, Yahoo Finance, or Morningstar, the default figure shown is the levered beta, which directly reflects the company’s debt situation.
In contrast, Asset Beta analysis provides a clearer view of a company’s inherent business risk by excluding the effects of financial leverage. It focuses solely on the volatility of the company’s core business operations. Using Tesla again, its asset beta would highlight the risks tied to the electric vehicle market without the influence of its debt levels. This distinction is significant; while equity beta reveals how a company’s capital structure impacts its stock’s sensitivity to market changes, asset beta captures the fundamental risk of the company’s assets themselves. By examining both betas, investors can make more informed decisions based on their risk tolerance and investment strategies, understanding not just how a company might react to market swings but also the underlying operational risks that drive its business.
WHY EQUITY BETA ANALYSIS MATTERS?
Why Equity Beta analysis matters is key for investors to assess stock market risk. Equity beta helps determine how much a stock’s price fluctuates compared to the market. For example, Tesla, in the cyclical electric vehicle industry, has a higher beta, meaning its stock is more volatile and sensitive to economic conditions. In contrast, companies like Verizon Communications in stable sectors, such as utilities, have lower betas, indicating less price fluctuation. While asset beta reveals operational risk, it’s less used for comparisons because it doesn’t reflect the impact of leverage on stock volatility, making equity beta the go-to measure for investors.
HOW TO CALCULATE EQUITY BETA?
Equity beta of a company can be calculated using regression analysis approach as described below:
1. REGRESSION ANALYSIS: The most common method involves plotting the stock’s returns against the market’s returns (e.g., S&P 500) over a certain period. Using statistical software or slope function in Microsoft excel, you can run a regression analysis to determine the slope of the line, which represents the stock’s beta. This method is widely used and provides a historical view of how the stock has reacted to market changes.
Let’s understand the Beta calculation using Regression analysis for Walmart Inc. using the monthly stock price of Walmart Inc. and S&P 500 for the last 5 years. You can download the template for the beta analysis here.
Step 1: First collect the 5-year monthly stock price data for Walmart Inc. and S&P 500 index from any financial website like Yahoo Finance as below. Calculate the % change in price for both Walmart Inc. and S&P500 index.
| Date | S&P 500 Index | Walmart Stock Price ($) | % change in Walmart Inc Price | % change in S&P index |
| Sep 1, 2019 | 2,976.74 | 36.62 | ||
| Oct 1, 2019 | 3,037.56 | 36.18 | -1% | 2% |
| Nov 1, 2019 | 3,140.98 | 36.75 | 2% | 3% |
| Dec 1, 2019 | 3,230.78 | 36.67 | 0% | 3% |
| Jan 1, 2020 | 3,225.52 | 35.48 | -3% | 0% |
| Feb 1, 2020 | 2,954.22 | 33.37 | -6% | -8% |
| Mar 1, 2020 | 2,584.59 | 35.22 | 6% | -13% |
| Apr 1, 2020 | 2,912.43 | 37.84 | 7% | 13% |
| May 1, 2020 | 3,044.31 | 38.62 | 2% | 5% |
| Jun 1, 2020 | 3,100.29 | 37.45 | -3% | 2% |
| Jul 1, 2020 | 3,271.12 | 40.46 | 8% | 6% |
| Aug 1, 2020 | 3,500.31 | 43.42 | 7% | 7% |
| Sep 1, 2020 | 3,363.00 | 43.93 | 1% | -4% |
| Oct 1, 2020 | 3,269.96 | 43.56 | -1% | -3% |
| Nov 1, 2020 | 3,621.63 | 47.97 | 10% | 11% |
| Dec 1, 2020 | 3,756.07 | 45.26 | -6% | 4% |
| Jan 1, 2021 | 3,714.24 | 44.27 | -2% | -1% |
| Feb 1, 2021 | 3,811.15 | 40.94 | -8% | 3% |
| Mar 1, 2021 | 3,972.89 | 42.8 | 5% | 4% |
| Apr 1, 2021 | 4,181.17 | 44.27 | 3% | 5% |
| May 1, 2021 | 4,204.11 | 44.94 | 2% | 1% |
| Jun 1, 2021 | 4,297.50 | 44.8 | 0% | 2% |
| Jul 1, 2021 | 4,395.26 | 45.28 | 1% | 2% |
| Aug 1, 2021 | 4,522.68 | 47.05 | 4% | 3% |
| Sep 1, 2021 | 4,307.54 | 44.44 | -6% | -5% |
| Oct 1, 2021 | 4,605.38 | 47.64 | 7% | 7% |
| Nov 1, 2021 | 4,567.00 | 44.84 | -6% | -1% |
| Dec 1, 2021 | 4,766.18 | 46.13 | 3% | 4% |
| Jan 1, 2022 | 4,515.55 | 44.76 | -3% | -5% |
| Feb 1, 2022 | 4,373.94 | 43.27 | -3% | -3% |
| Mar 1, 2022 | 4,530.41 | 47.67 | 10% | 4% |
| Apr 1, 2022 | 4,131.93 | 49.17 | 3% | -9% |
| May 1, 2022 | 4,132.15 | 41.34 | -16% | 0% |
| Jun 1, 2022 | 3,785.38 | 39.21 | -5% | -8% |
| Jul 1, 2022 | 4,130.29 | 42.59 | 9% | 9% |
| Aug 1, 2022 | 3,955.00 | 42.75 | 0% | -4% |
| Sep 1, 2022 | 3,585.62 | 42.01 | -2% | -9% |
| Oct 1, 2022 | 3,871.98 | 46.11 | 10% | 8% |
| Nov 1, 2022 | 4,080.11 | 49.37 | 7% | 5% |
| Dec 1, 2022 | 3,839.50 | 45.93 | -7% | -6% |
| Jan 1, 2023 | 4,076.60 | 46.78 | 2% | 6% |
| Feb 1, 2023 | 3,970.15 | 46.21 | -1% | -3% |
| Mar 1, 2023 | 4,109.31 | 47.94 | 4% | 4% |
| Apr 1, 2023 | 4,169.48 | 49.29 | 3% | 1% |
| May 1, 2023 | 4,179.83 | 47.95 | -3% | 0% |
| Jun 1, 2023 | 4,450.38 | 51.51 | 7% | 6% |
| Jul 1, 2023 | 4,588.96 | 52.39 | 2% | 3% |
| Aug 1, 2023 | 4,507.66 | 53.29 | 2% | -2% |
| Sep 1, 2023 | 4,288.05 | 52.6 | -1% | -5% |
| Oct 1, 2023 | 4,193.80 | 53.74 | 2% | -2% |
| Nov 1, 2023 | 4,567.80 | 51.21 | -5% | 9% |
| Dec 1, 2023 | 4,769.83 | 51.85 | 1% | 4% |
| Jan 1, 2024 | 4,845.65 | 54.55 | 5% | 2% |
| Feb 1, 2024 | 5,096.27 | 58.04 | 6% | 5% |
| Mar 1, 2024 | 5,254.35 | 59.59 | 3% | 3% |
| Apr 1, 2024 | 5,035.69 | 58.98 | -1% | -4% |
| May 1, 2024 | 5,277.51 | 65.35 | 11% | 5% |
| Jun 1, 2024 | 5,460.48 | 67.52 | 3% | 3% |
| Jul 1, 2024 | 5,522.30 | 68.44 | 1% | 1% |
| Aug 1, 2024 | 5,648.40 | 77.01 | 13% | 2% |
| Sep 1, 2024 | 5,762.48 | 80.75 | 5% | 2% |
Source data:
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/%5EGSPC/history/?period1=1567296000&period2=1727654400&frequency=1mo
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/WMT/history/?frequency=1mo&period1=1567296000&period2=1727654400
**
2. CALCULATE EQUITY BETA
Method 1: Using the slope function in Excel
Equity Beta can be calculated using the slope function in Excel by selecting the y-axis as the % change in Walmart Inc.’s price and the x-axis as the % change in S&P500 index price as follows.
Beta =Slope (known_ys,known_xs)
Where
- Known_ys = % change in Walmart Inc.’s price
- Known_xs = % change in S&P500 price
Beta for Walmart = 0.51
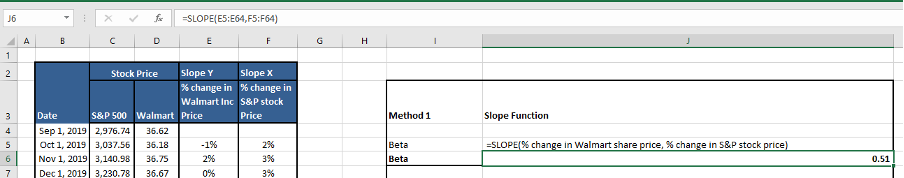
Where,
E5:E64 is the column in which % change in Walmart Inc.’s price is calculated for 5 years
F5:F64 is the column in which % change in S&P500 price is calculated for 5 years.
This is the most used method due to its simplicity and easy access to price data.
**
Method 2: Correlation and Standard Deviation
Beta = Correlation (Ri, Rm) * σi/σm
Where,
- Correlation(Ri,Rm) is the correlation between the stock’s return (Ri) and the market’s return (Rm),
- σi is the standard deviation of the stock’s returns,
- σm is the standard deviation of the market’s returns.
Beta= 0.492336698* 0.05381322/ 0.052004105 = 0.51
Where,
Correlation = 0.492336698
The standard deviation of Walmart stock return = 0.05381322
The standard deviation of market returns = 0.052004105
**
Method 3: Covariance and Variation
Beta = Cov (Ri, Rm)/ Var(Rm)
Where,
- Cov(Ri,Rm) is the covariance between the stock’s returns (Ri) and the market’s returns (Rm),
- Var(Rm) is the variance of the market’s returns.
Beta= 0.001377808/ 0.002704427 = 0.51
Where,
Cov(Ri, Rm) = 0.001377808
Var(Rm) = 0.002704427
Hence we can see that we get the same results from all the three methods discussed above.
**
UN-LEVERING AND RE-LEVERING BETA ANALYSIS:
Beta is a measure of a stock’s volatility compared to the broader market, which helps investors understand risk. When calculating equity beta, which includes the impact of a company’s debt, we need to account for leverage. By un-levering beta, we remove the effect of debt to focus on the asset beta or the company’s operational risk. Then, by re-levering, we can adjust the asset beta to reflect the company’s or target capital structure.
Here’s how we can calculate Walmart Inc.’s beta using this method:
Step 1: Gather Inputs
We need the following data for Walmart Inc.:
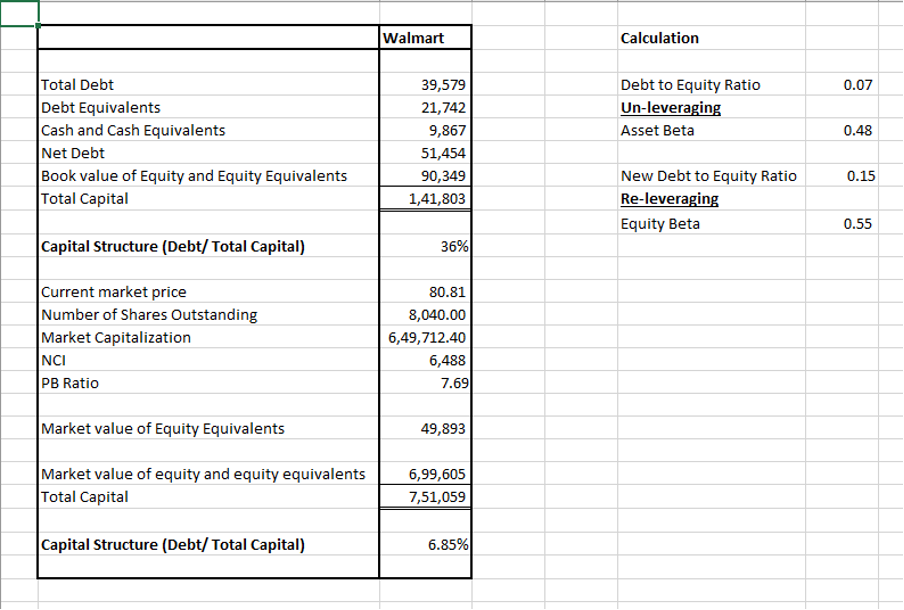
- Equity Beta (Levered Beta): This is the beta that reflects both operational risk and financial leverage (debt). Walmart’s equity beta is 0.51, which we can get from our above analysis.
- Net Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Walmart’s current capital structure net debt should be compared to its equity. Walmart Inc. has a net debt of $51,454 million calculated by adding total debt and debt equivalents and subtracting cash and cash equivalents. The market value of equity and equity equivalents is $6,99,605 million calculated by adding the market capitalization and market value of equity equivalents.
Hence the net debt-to-equity ratio comes to 7%.
Step 2: Un-levering Beta (Finding Asset Beta)
To find Apple’s asset beta (which reflects its business risk without the impact of debt), we use the formula:
Asset Beta = Equity Beta / 1+ (Debt/Equity)
Now, let’s plug in the values:
Asset Beta= 0.51/1+(0.07/1)
= 0.48
So, the asset beta for Walmart is approximately 0.48. This beta represents Walmart’s operational risk without the influence of debt.
Step 3: Re-levering Beta (Adjusting for Capital Structure)
If Walmart changes its capital structure or if you want to adjust the beta for different debt levels, you would re-lever the asset beta using the company’s debt-to-equity ratio. For instance, let’s assume Walmart is considering increasing its debt-to-equity ratio to 15%.
To re-lever the beta, we use the formula:
Equity Beta = Asset Beta × (1+ (Debt/Equity)
Plugging in the values:
Equity Beta = 0.48*(1+(0.15/1)
= 0.55
So, if Walmart increases its debt-to-equity ratio to 15%, the new equity beta would be approximately 0.55. This means that with more debt, Walmart’s stock would become more volatile and riskier for equity investors.
This method is important because un-levering beta reveals a company’s operational risk without the influence of debt, making comparisons across companies easier. Re-levering beta adjusts for debt, providing a clearer view of stock risk for investors. For instance, with increased debt, Walmart’s equity beta rises from 0.51 to 0.55, highlighting how leverage amplifies risk.
PRACTICAL APPLICATION OF BETA ANALYSIS IN PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT
Equity Beta is vital for portfolio management. Investors seeking higher returns may gravitate toward high-beta stocks, anticipating stronger gains when markets are bullish. However, these stocks also expose them to higher losses when the market declines. Conversely, low-beta stocks offer stability, making them attractive to risk-averse investors, especially during economic downturns.
Example for the above is Tesla vs. Verizon.
Tesla, known for its high-growth potential, has a beta significantly above 1 around 2.30, reflecting the stock’s strong correlation with market fluctuations. The company’s performance is often tied to consumer sentiment, economic cycles, and innovation in the electric vehicle sector. In contrast, Verizon, a telecommunications giant, has a lower beta of around 0.41 because its services are considered essential, providing more consistent cash flows and lower volatility.
CONCLUSION
Equity Beta analysis is a valuable tool for investors looking to understand a stock’s market sensitivity. Whether you aim for growth with high-beta stocks like Tesla or prefer stability with low-beta stocks like Verizon, beta analysis helps you make informed decisions to match your risk tolerance and investment strategy. By understanding how different companies react to market changes and differentiating between equity and asset beta, investors can build more resilient portfolios and better anticipate stock price movements.


