WHAT IS DEFERRED REVENUE?
In accrual accounting Deferred Revenue also known as the Deferred income, unearned income or unearned revenue is the advance payment received by a company for the products to be delivered or services to be performed in the future. In short, it is the money received by the company for the products or services which has yet not been earned. Revenue is recognized only when it is earned as per the accrual accounting. It is recorded as a liability on its Balance Sheet until delivery of products is made or services is rendered according to the Revenue Recognition principle. Once the products delivered or services are rendered the revenue earned is recognized in the Revenue or sales to customer account on its Income statement and a similar amount is reduced from the deferred revenue account.
REAL LIFE EXAMPLE OF DEFERRED REVENUE RECOGNITION BY COMPANIES
Let us see the Balance sheet of Alphabet Inc. recognizing the deferred revenue.
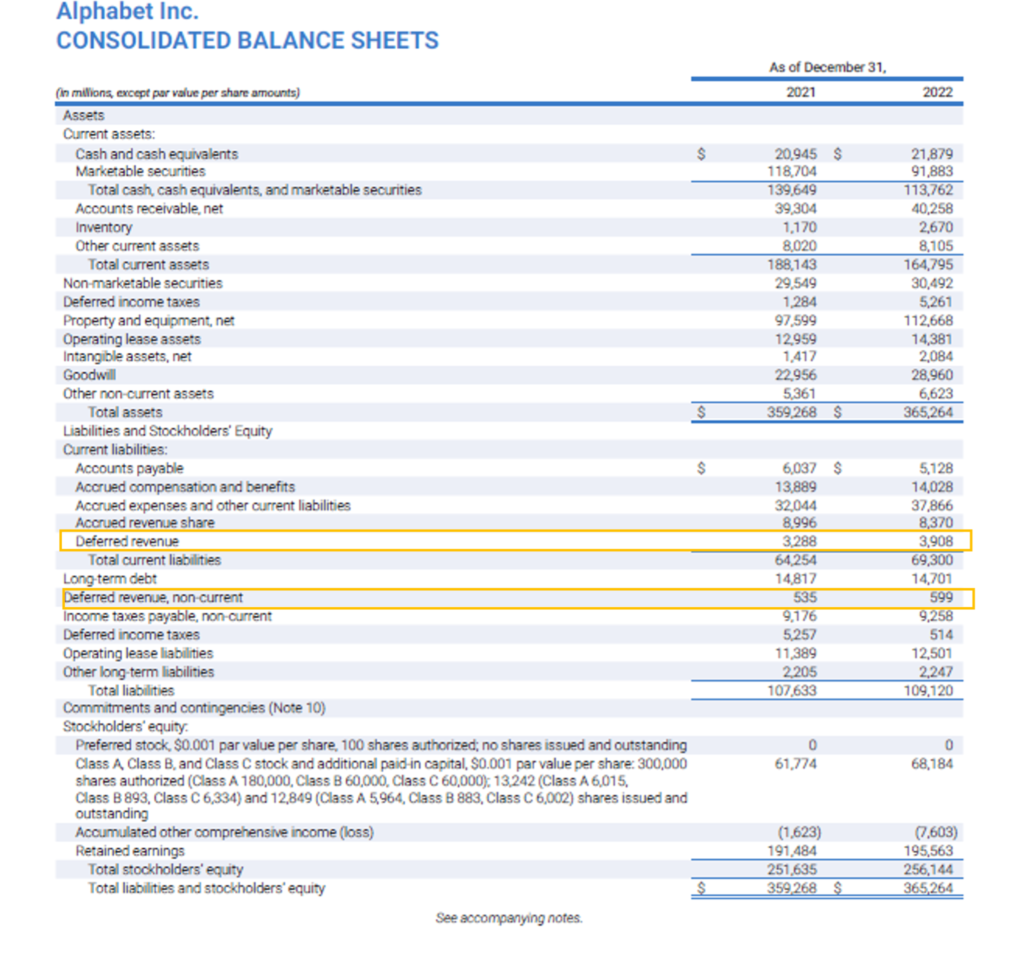
Source: https://abc.xyz/investor/
From the above Balance sheet, we can observe that Alphabet Inc. has recognized deferred revenue under current and non-current liabilities. If the company expects to deliver the goods or render the services for advance received within 12-month period, it classifies it as current liabilities. However, if some part of advance received pertains to product or service to be delivered beyond a period of 12-month, it is classified as non-current liability.
REASON BEHIND CLASSIFICATION OF DEFERRED REVENUE AS A LIABILITY?
Deferred revenue is classified as a liability by the company because it has not yet earned the money received by it and has an obligation to the customer in the form of products or services owed. Since there is still the possibility that the goods or services may not be delivered to the customer or the order might get cancelled by the customer, the payment is considered as a liability by the company till the time it delivers the products or renders the service.
Some of the reasons why deferred revenue is classified as a liability by a company are as follows:
- It has a debt to the customer- Since the company has not yet delivered goods or rendered services to the customer, the customer may demand a refund back or cancel the order anytime, or the company due to any situation may fail to deliver its obligation, and as a result the company have to return the advance received back to the customer. We all know that a Liability in accrual accounting is a company’s future obligation based on previous business activity. Since deferred revenue is a result of advance payment received now that fixes the companies obligation to provide goods or services to customers in future, it is classified as a liability.
- It cannot recognize revenue before it is earned- A company is prevented from recognizing revenue as per the accounting guidance until the company has fulfilled the revenue recognition requirements. In case of advance payments received, the company has yet not performed its contractual obligation of providing goods or rendering services and hence not allowed to recognize revenue.
- In accounting it is the most conservative approach- In accounting revenue is recognized only when it has been actually earned rather than recognizing it when cash is received. This prevents the company from overstating its revenue when advance cash is received and understating the revenue during the period where it has actually been earned. This is the conservative accounting approach where the loses are recorded when they are discovered and gains are recognized when they are realized fully.
- It follows the matching principle in accounting- As per the matching principle in accounting expenses are reported at the same time as the revenues they are related to. As per deferred revenue concept, revenue is recognized as a liability and only taken to revenue account when the company actually fulfils its obligation towards the customer.
CAN WE RECOGNIZE DEFERRED REVENUE IN CASH BASIS ACCOUNTING?
In the cash basis accounting all the revenue is recognized when it is received while the expenses are recorded only when they are paid. The cash basis is completely different from accrual accounting since in accrual accounting revenue is recognized when it is actually earned rather than received and expenses are recorded when they are due rather than when paid.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEFERRED REVENUE AND ACCRUED REVENUE
Deferred revenue is a concept opposite to accrued revenue. While the accrued revenue is the revenue that is earned (goods or services provided to the customers), but has not yet been received (such as accounts payable) while the deferred revenue is revenue that is received, but not yet earned (goods or services yet to be provided to the customers).
ACCOUNTING FOR DEFERRED REVENUE
Normally receiving payments is considered as an asset, however prepayments are considered liability since it is not yet earned and the company still has obligation towards the customers. The deferred revenue is thus classified as a liability in the balance sheet and not as an asset. The deferred revenue is taken to revenue account in income statement only after the customers receives the goods or services.
For example, a country club collects a one-time annual fees from its members’ of $1200 immediately when the member approaches it to join the club. Since the club will be providing the service throughout the year, the cash received is recognized as a deferred revenue at the point when it is received. The deferred revenue is recognized as a liability and not as revenue in the income statement. Only when the income is earned, the liability is decreased and income is recognized. At the time of the receipt of annual subscription the accounting entry to be passed by the club is as follows.
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Cash | 1200 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 1200 |
Every member has received the benefit of having enjoyed the membership of the club for one month, at the end of the first month. Since the country club has fulfilled one month of its requirement to offer membership benefits to its members, it shall recognize 1/12th of the annual fees as Revenue and decrease the deferred revenue by the same amount. The accounting entry for the same shall be as follows.
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Deferred Revenue | 100 | |
| Revenue | 100 |
Every month the club shall pass the same accounting entry as above, until the deferred revenue account balance is zero and the revenue account balance is $1200.
COMMON EXAMPLES OF DEFERRED REVENUE
Deferred revenue recognition is common in case of services or products that are subscription based and require prepayments. Some examples of deferred revenue are prepayments received for newspaper subscription, subscription to use a software, prepaid insurance and advance rent receipts.
IMPACT OF DEFERRED REVENUE ON CASH FLOW STATEMENTS
Deferred revenue’s impact on the income statement and balance sheet has been discussed above in details. We hence, move forward to understand its impact on the Cash Flow Statement of the company. Considering the above example of country club, when the club receives the upfront advance payment of the membership fees for the entire year of $1200, it would result in increase in the current liabilities by $1200 and hence increase in Cash from Operating activities by $1200. At the receipt of upfront payment, the net income shall be $0. However, with the passage of each subsequent month the current liabilities shall reduce by $100 and at the same time Net Income shall increase by $100 thereby offsetting each other and having no impact on the Cash flow statement. Thus, cash flow statement will have impact only when advance is received by the company.
IMPACT OF DEFERRED REVENUE ON WORKING CAPITAL
Since deferred revenue is a liability that is earned, it reduces the working capital of the company. Working capital is calculated as operating current assets less operating current liabilities. In this formula since operating current liabilities is deducted, it will lower the overall working capital requirement of the company.
DEFERRED REVENUE VS. DEFERRED EXPENSES
Deferred revenues refer to cash received for products or services to be provided to customers in future, whereas deferred expenses refer to cash expended for products or services not yet received by a company. For example, for a software company, deferred expenses shall be advance payment of rent made for use of property or land whereas the deferred revenue shall be advance received from the customers for annual subscription for the software supplied by it. The deferred revenue is classified as a liability and deferred expenses is classified as an asset in the balance sheet. Only once the goods or services are actually supplied by the company, it reduces its deferred revenue to recognize Revenue to that extend and similarly, only once goods or services are actually received by the company, it recognizes the expense and reduces the deferred expense by that extend.
DIFFERENT METHODS OF REVENUE RECOGNITION UNDER GAAP
Different methods of revenue recognition are allowed by the Accounting standards according the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), depending on the industry the company operates in and some specific circumstances.
As per the accounting standards a contractor for example can recognize revenue either using the percentage-of-completion method or the completed contract method. Under the percentage-of-completion method, revenue is recognized when certain milestones are met by the company. Under the completed-contract method, revenue is recognized only when the entire contract is completed and the contract terms are fulfilled by the company. Due to this major recognition difference the reported revenue under the completed-contract method is lower and deferred revenue is higher than the percentage-of-completion method.
Due to different methods of revenue recognition used by different companies, the financial statement of one company using one method of revenue recognition appears different from the other company using a different accounting method. Each method of revenue recognition results in a different amount recorded as deferred revenue although the total amount of the financial transaction being same in all the methods.
IS DEFERRED REVENUE AN OPERATING OR A NON-OPERATING LAIBILITY?
Amount owed by the company resulting from the normal operations of the company is called as operating liabilities whereas the amounts owed resulting from things not related to company’s normal operations is called as non-operating liabilities. Since deferred revenue results from the advance received for the future supply of goods or rendering of services by the company, it is classified as operating liability. Examples are advance rent received or upfront annual subscription received by software companies or AMC.
Conclusion
Deferred Revenue is a great source of cash flows from a business operating perspective since the cash is received upfront for goods and services to be delivered later. There are lots of technology companies who work on this model which ensures a revenue continuity as well since there are lock-ins to annual subscriptions that is embedded within the contract with the company. However, the business will still need to deliver on the goods and services it has contracted the customer for and therefore is important to remember it is a liability after all.


