(Annual report, Form 10-K, Form 20-F)
INTRODUCTION
Investing in a company for example Microsoft requires more than just knowing its products—you need to understand its financial pulse. A smart investor digs into the company’s financial health to evaluate potential risks and returns. Reviewing key financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement shows how Apple has performed over the years, how it’s doing in recent quarters, and whether it’s hitting its financial targets.
A crucial resource in this analysis is the annual report. Microsoft’s annual report provides a wealth of financial insights for investors, from revenue trends to future strategies, helping you make informed decisions about whether to invest. But even if you’re a Microsoft employee, the annual report offers valuable insights into the company’s performance and how your contributions align with its goals. It’s not just for financial experts either—anyone can glean important takeaways from Microsoft’s annual report, using it to understand the company’s direction better and even advocate for career growth based on these insights.
In this article let’s delve deep into the different information an annual report provides to its readers and how can it be useful for them.
WHAT IS AN ANNUAL REPORT?
An annual report acts as a company’s window to the world, offering a comprehensive look into its operations, financial health, and future direction. Microsoft’s annual report, for example, provides a detailed overview that helps current and potential investors make informed decisions. Typically split into two parts, the first section tells Microsoft’s story over the past year, featuring insights from key executives like Satya Nadella, along with compelling visuals and forward-looking statements. The second section dives into the financial details, presenting key documents such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. This blend of narrative and data not only meets legal obligations but also serves as a strategic marketing tool, giving shareholders and the public deeper insights into Microsoft’s journey and goals.
The annual report, Form 10-K, and Form 20-F are essential documents for publicly traded companies to disclose financial and operational information. In the U.S., companies file Form 10-K with the SEC as a detailed summary of their yearly performance, including financial statements, risks, and management analysis. Foreign companies listed on U.S. exchanges use Form 20-F to provide similar disclosures, ensuring compliance with SEC regulations. Both forms serve as critical components of the company’s annual report, offering transparency to investors and aligning with international reporting standards where necessary.
INFORMATION CONTAINED IN AN ANNUAL REPORT
For investors, analysts, or anyone interested in a company, mastering how to read this document is crucial for making informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of key sections to focus on and how to extract meaningful insights.
1. BEGIN WITH THE CEO’S LETTER:
The CEO’s letteralso known as Letters to shareholders is the heart of the annual report, setting the tone for the entire document. Take Microsoft’s annual report, for instance. Satya Nadella’s letter provides a personal touch, reflecting on the company’s performance over the past year, recent successes like advancements in AI, and challenges such as adapting to market shifts and the exciting future ahead. This section offers valuable context, giving readers insight into how Nadella views Microsoft’s strengths, weaknesses, and strategic direction. It frames the rest of the report, offering a roadmap of where Microsoft is headed and how its leadership envisions navigating the future. We can also find the snapshot of the letter to shareholders having the signature of the CEO, CFO, or chairman below.

Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
When diving into CEO’s letter, keep an eye out for:
- Vision and Strategy: What bold plans and strategic goals does the CEO unveil?
- Achievements: What impressive milestones and victories are showcased?
- Challenges: What major hurdles has the company overcome, and how did it tackle them?
- Financial Summary: How does the CEO paint a picture of the company’s financial performance?
- Future Outlook: What exciting prospects and plans lie ahead for the company?
- Strengths and Weaknesses: How does the CEO highlight the company’s key advantages and areas needing attention?
- Key Initiatives: What groundbreaking projects and strategies are on the horizon?
- Shareholder Concerns: How does the CEO address and reassure shareholder concerns?
**
2. BUSINESS:
The business section of an annual report provides a dynamic overview of a company’s year, capturing its core operations, major milestones, and financial highlights. It reflects on the company’s strategic direction, significant achievements, and any unforeseen challenges faced. Unlike the letter to shareholders, which typically conveys a more personal and strategic perspective from top executives, the business section focuses on a factual and comprehensive summary of the company’s performance and key developments.
Here is a short summary of each subheading from the business section of the document:
- Company Overview: Microsoft empowers individuals and organizations globally through AI, cloud services, and comprehensive software solutions.
- Product Offerings: Includes products like Azure, Office 365, Dynamics 365, and LinkedIn, addressing productivity, collaboration, and cloud computing.
- Growth Strategy: Focuses on AI and cloud innovation while continuously expanding its user base across industries.
- Key Segments: Microsoft’s business is divided into three core segments: Productivity & Business Processes, Intelligent Cloud, and More Personal Computing.
- Sustainability: Microsoft aims to be carbon negative by 2030, focusing on environmental sustainability in its operations.
- Competition: Microsoft faces competition in various sectors: Windows competes with Apple’s macOS and Google’s Chrome OS, Surface devices with Apple and PC makers, and Xbox with gaming platforms from Amazon, Sony, and Nintendo. Bing challenges Google’s search engine and Meta’s social media, while LinkedIn contends with other professional networks and job boards.
- Customers: Microsoft’s customers range from individual consumers to large enterprises, public institutions, developers, and OEMs. The company ships products promptly upon order receipt, making backlog minimal.
- Available Information: Microsoft provides a variety of investor information through its Investor Relations website, including reports, financial metrics, press releases, and corporate governance details. The site also features announcements of investor events, archives, and email alerts. Additionally, Microsoft shares Corporate Social Responsibility updates on its Reports Hub and uses social media for public communication, which may include material information for investors.
**
3. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS (MD&A):
The MD&A section aims to provide insights into Microsoft’s financial condition, operational results, segment reporting performance, competition and non-GAAP metrics. It discusses performance for the fiscal year ending June 30, 2023, and encourages readers to consider it alongside the consolidated financial statements for a comprehensive understanding.
Below is the key information presented under MD&A section of the annual report:
- Financial Highlights: For fiscal year 2023, Microsoft reported a 7% increase in overall revenue, driven by growth in Intelligent Cloud and Productivity & Business Processes, while experiencing a decline in More Personal Computing. Key figures include a 22% rise in cloud revenue to $111.6 billion and a decrease of 25% in Windows OEM revenue.
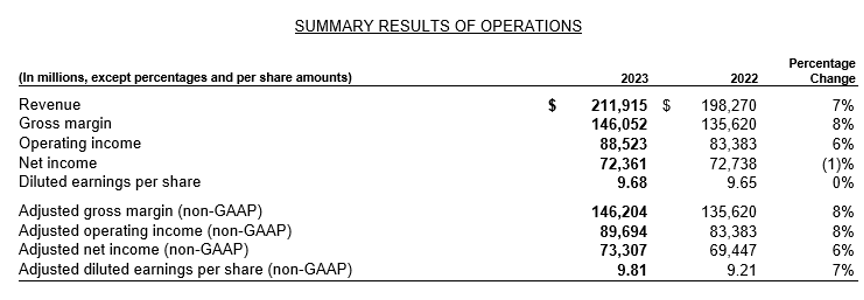
- Industry Trends: Microsoft identifies its industry as dynamic and competitive, with rapid technological advancements and shifting business models. The company sees each shift as an opportunity to innovate and meet changing customer demands through research and development.
- Economic Conditions, Challenges, and Risks: The report notes that the software and cloud markets are competitive and influenced by macroeconomic factors. Microsoft emphasizes the importance of adapting to these challenges while continuing to invest in cloud and AI infrastructure.
- Operating Segments: Microsoft’s performance is reported across three segments: Productivity and Business Processes, Intelligent Cloud, and More Personal Computing, allowing for a comprehensive financial view and alignment of strategies across the organization.
- Metrics: The MD&A highlights the importance of various metrics to assess business performance, including Microsoft Cloud revenue, Office Commercial products revenue, and Dynamics products growth. These metrics are essential for evaluating progress and guiding resource allocation.
- Critical Accounting Estimates: Microsoft discusses the significance of critical accounting estimates, particularly in areas like revenue recognition and impairment, emphasizing that these estimates can significantly impact financial results. Example shown for Impairments below.

This structured approach in the MD&A section provides stakeholders with a clearer understanding of Microsoft’s financial health and strategic direction.
**
4. RISK FACTORS:
Every company faces risks, and this section outlines the significant risks that could affect business operations and financial results. While some risks are industry-specific, others, like economic downturns or regulatory changes, are universal. Understanding these risks will help you gauge the company’s potential vulnerabilities.
For example, Microsoft’s annual report, outlines its exposure to various economic risks, including foreign exchange rates, interest rates, credit risk, and equity prices. Microsoft utilizes derivative instruments to manage these risks, although such exposure may still impact its financial statements. The report also includes a sensitivity analysis that estimates potential impacts on future earnings and fair values based on hypothetical changes in market rates, revealing significant potential losses from currency fluctuations, interest rate increases, and equity market declines.

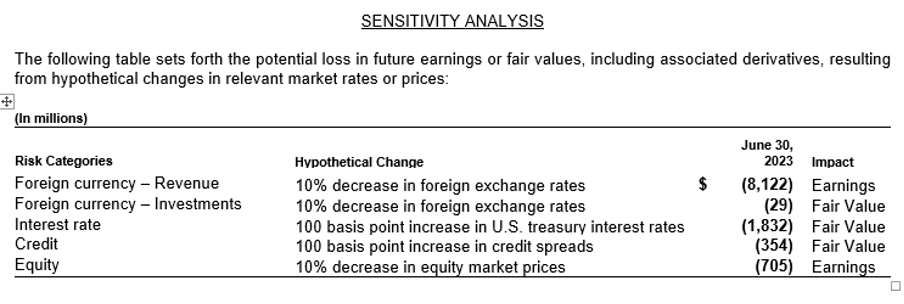
Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
**
5. AUDITED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:
The financial statements are the backbone of an annual report, providing essential data to assess a company’s financial health. Focusing on key statements will give you a clear picture of a company’s performance and stability. Using Microsoft as an example, here’s what to look for:
a. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement): This statement outlines Microsoft’s revenue, expenses, and the resulting profit or loss for the year. When reviewing this, focus on trends in revenue growth, profit margins, and how well expenses are managed. For example, Microsoft’s growing revenue from cloud services like Azure has significantly boosted profit margins in recent years, showcasing a positive trend in profitability.
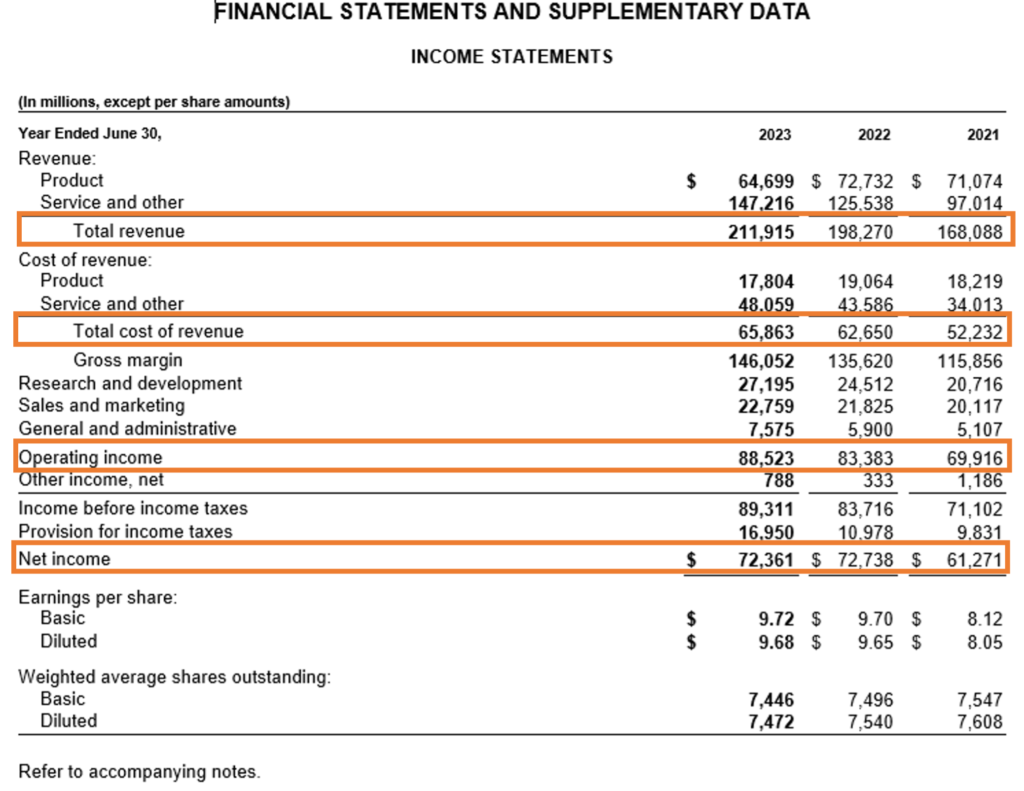
Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
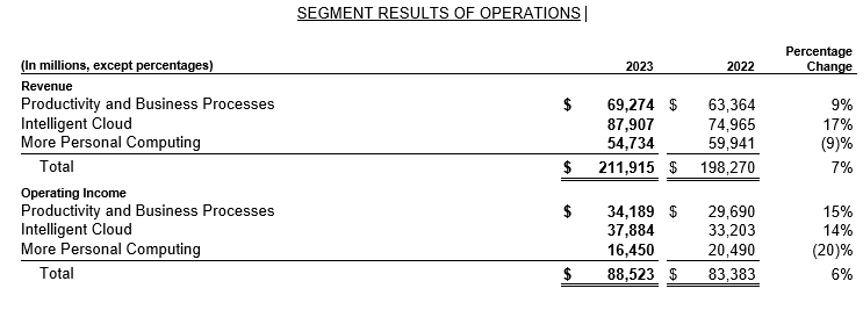
The Income Statement tells us the total revenue, total cost, and net profit earned by the company in any year. However, to get more details as to which product or service led to an increase to decline in revenue or which cost significantly increased from the previous year, one has to refer to the management discussion and analysis section and the notes to accounts section of the annual report.
For example, if one needs to know which business segment of Microsoft is resulting in an increase or decrease in revenue as compared to the previous year one can refer to the following section of MD&A, where we can see that Intelligent cloud has led to 17% increase in revenue and increase in operating income by 14%. Whereas, more personal computing has led to a 7% increase in revenue and a decline in operating income by 20%, which means that the operating cost related to this segment is more than the revenue.
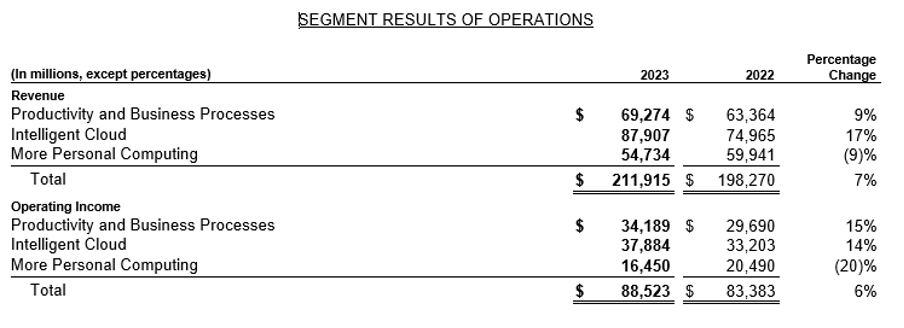
Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
b. Comprehensive Income Statement: Unlike the traditional income statement, the comprehensive income statement captures all changes in equity from non-operational gains or losses, such as currency fluctuations or unrealized gains or losses on investments. Reviewing this for Microsoft provides a fuller picture of total profitability beyond just operational performance.
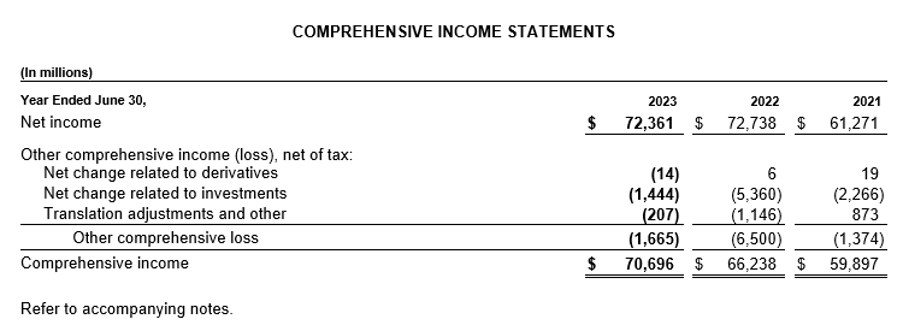
Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
c. Balance Sheet: The balance sheet presents a snapshot of Microsoft’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at the end of the fiscal year. Assets reveal what Microsoft owns, from cash reserves to intellectual property, while liabilities reflect its obligations, such as debts and loans. Shareholders’ equity represents the remaining value for shareholders after debts are paid. A strong balance sheet, like Microsoft’s, often indicates financial strength and stability.
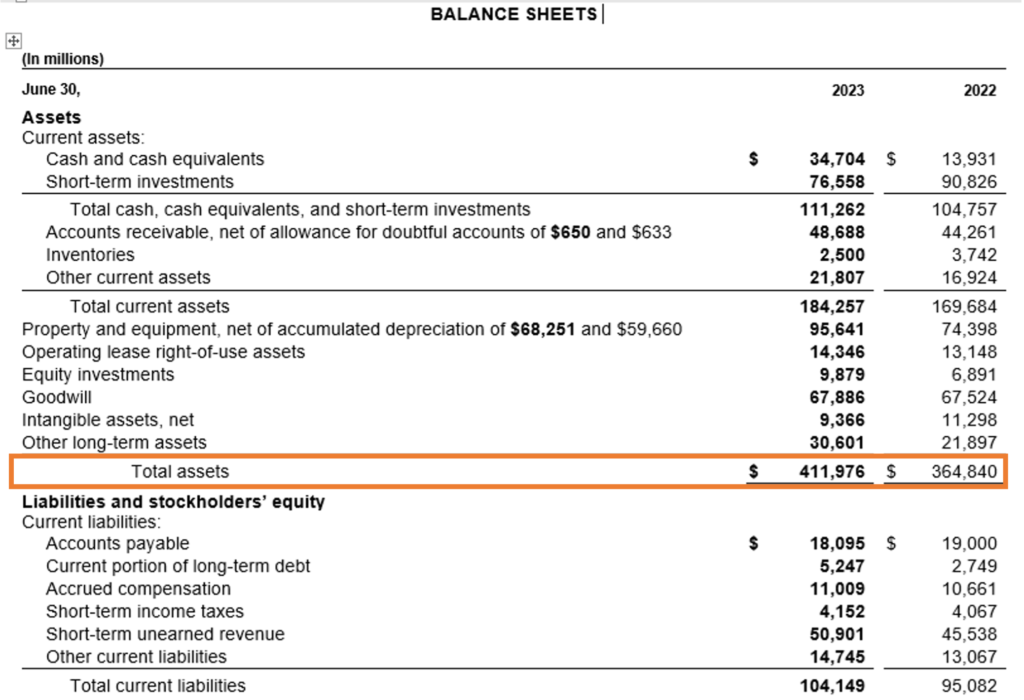
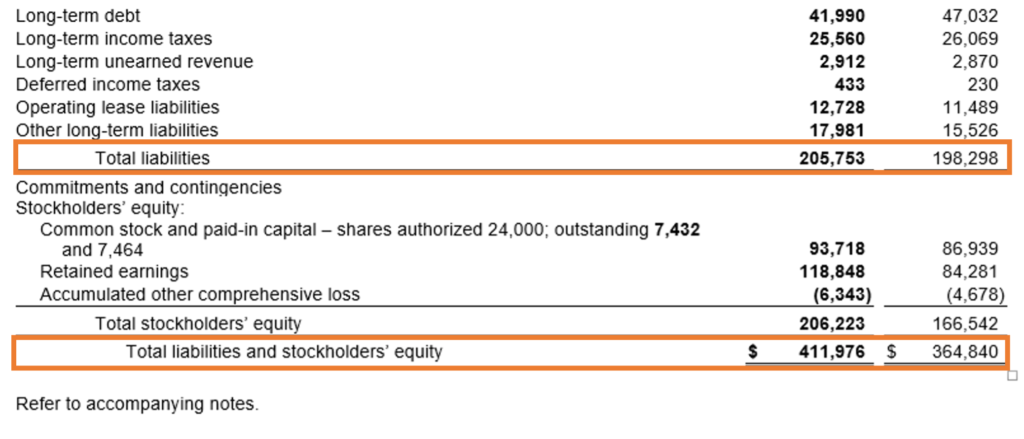
Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
From above we can get a broad idea of what is the financial position of Microsoft in terms of total assets held and total liabilities owed by it and also the shareholder’s position from the total equity. However, to know the details of what constitutes each of these assets and liabilities one has to refer to the notes to accounts section of the annual report discussed later.
d. Cash Flow Statement: Cash flow is crucial for understanding how well Microsoft manages its cash. This statement breaks down cash flow into three areas: operations, investing, and financing. A company like Microsoft, which consistently generates positive cash flow from operations, demonstrates strong financial health. Look at how cash is allocated—whether it’s being reinvested in technology, acquisitions, or returned to shareholders through dividends.
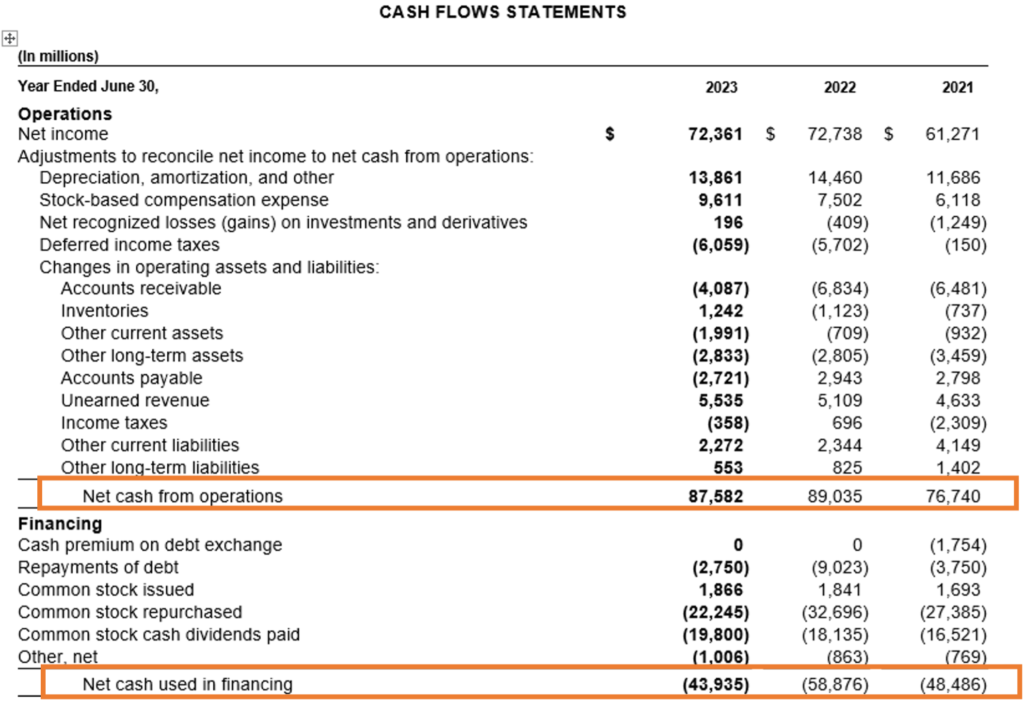
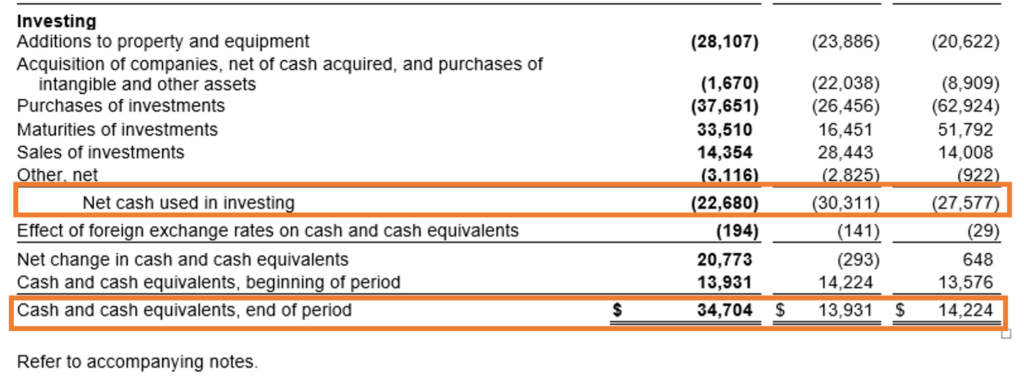
Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
From the above Cash Flow Statement, we can see that Microsoft has positive cash flow from operations and negative cash flow from investing and financing activities in all three years. However, the positive operating cash flow is big enough to make the cash at the year-end balance positive despite investing and financing cash flow being negative. Overall, this suggests that Microsoft is a financially stable company with strong operations, growth initiatives, and a focus on reducing liabilities or rewarding shareholders.
e. Statement of Shareholders’ Equity: This statement tracks changes in equity over the year, detailing factors such as retained earnings, dividends, and stock buybacks. For Microsoft, this would show how much profit has been reinvested into the company or distributed to shareholders. An increase in shareholders’ equity often signals strong company performance and shareholder value creation.
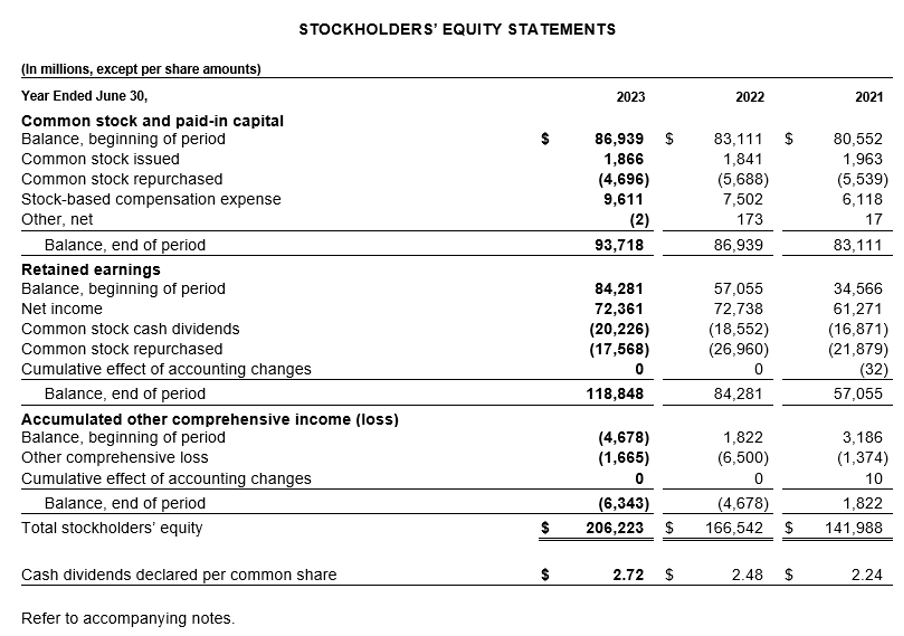
Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
From the above statement, we can see that Microsoft has been able to increase its dividend pay-out year after year and also increase its retained earnings and total stockholders’ equity reflecting its operational efficiency and strong commitment towards increasing its stockholders’ value.
Together, these financial statements offer a comprehensive view of Microsoft’s financial standing, helping investors make informed decisions.
**
6. NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:
The notes section offers additional context and details behind the numbers we see on the Income Statement and the Balance Sheet of the company. With Microsoft, you might find explanations of accounting policies, breakdowns of revenue sources, assets and liabilities or information about pending legal matters. These notes can clarify how specific figures are calculated and provide insight into the company’s operational nuances.
For example, let us take the Inventories figure from the balance sheet of Microsoft. We can see that the inventories balance is $2,500 million in the year 2023 and $3,742 million in the year 2022. However, to know how these Inventories figures are calculated we have to see the breakup of the Inventories in the notes to financial statements section of the annual report. Below is the snapshot from Note 1 Accounting Policies relating to Inventories which shows how inventories are recorded as per the accounting policy.

Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
Below is the break-up of the Inventories in Note 6 of the Notes to financial statements.

Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
We can also see the Business Combination details in the annual report of the company as below where we can see that Microsoft’s acquired Nuance Communications Inc. for $18.8 billion in 2022 to strengthen its cloud and AI offerings, especially in healthcare. Another key acquisition was ZeniMax Media Inc. for $8.1 billion in 2021, which bolstered Microsoft’s gaming division through its integration into the Xbox portfolio.
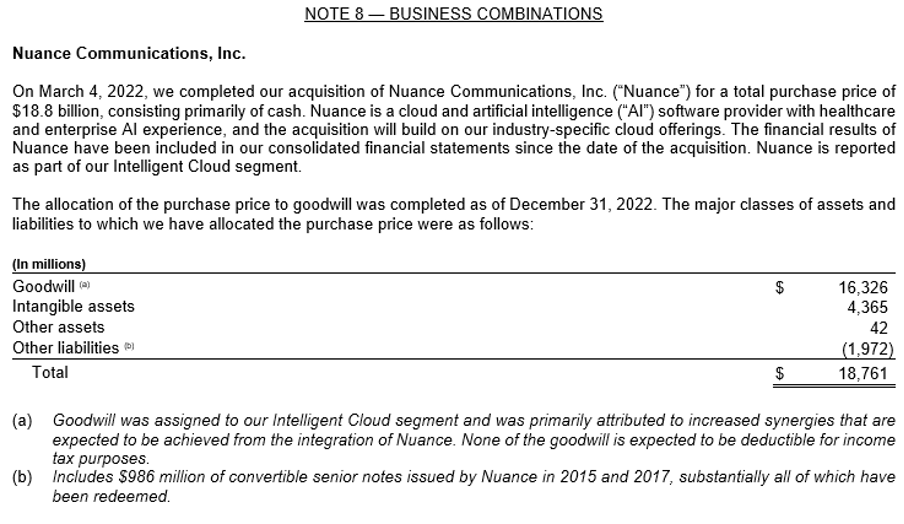


**
7. AUDITOR’S REPORT:
The auditor’s report in an annual report plays a crucial role in validating a company’s financial credibility. It’s an independent, expert assessment that ensures the financial statements—like the income statement and balance sheet—are accurate and free from material errors. This report gives shareholders and potential investors confidence that the company follows strict accounting standards and regulations. Essentially, it acts as a seal of trust, confirming that the company’s financial health is presented transparently, providing a solid foundation for investment decisions. Without it, the reliability of the financial data would be in question.
Below is the Auditor’s report of Microsoft.


Source: Annual Report https://www.microsoft.com/investor/reports/ar23/download-center/
**
8. INVESTOR RELATIONS: In this section of Microsoft’s annual report, the company provides multiple ways for investors to access important financial and strategic information. The Investor Relations website offers resources such as quarterly and annual reports, press releases, and corporate governance details. Investors can also access updates on financial performance, business strategies, and upcoming conferences. Microsoft enables investors to sign up for real-time alerts and provides various reports, including on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) topics like sustainability and ethical practices.
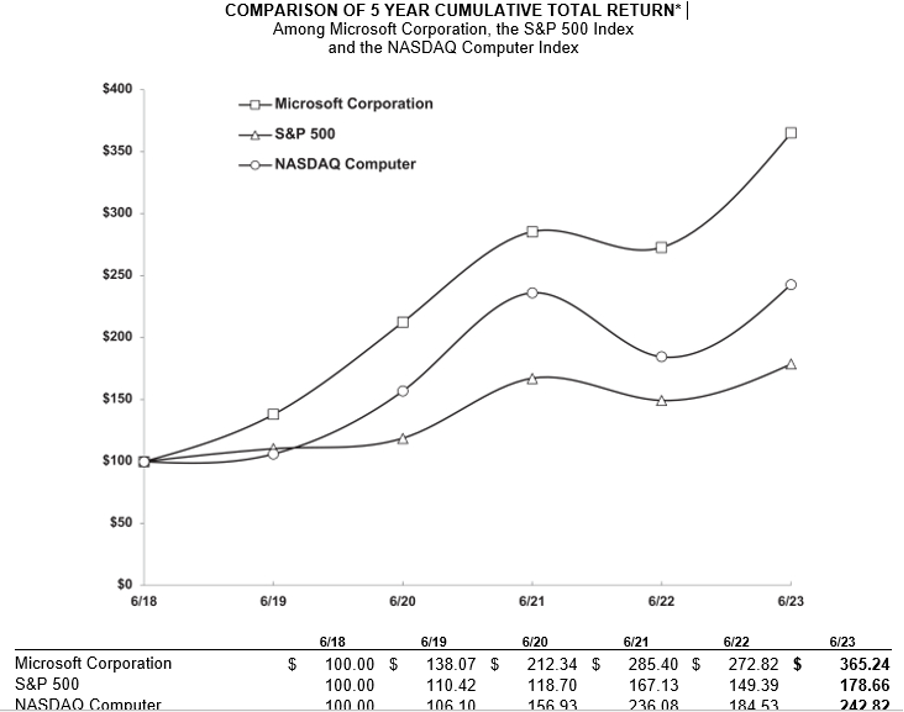
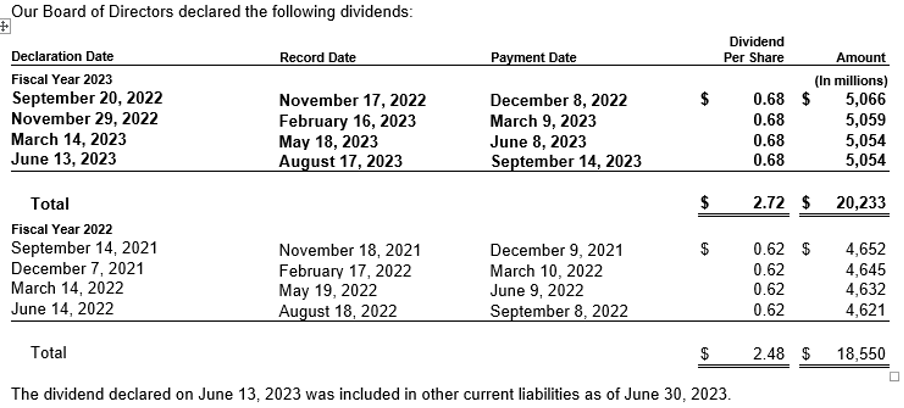
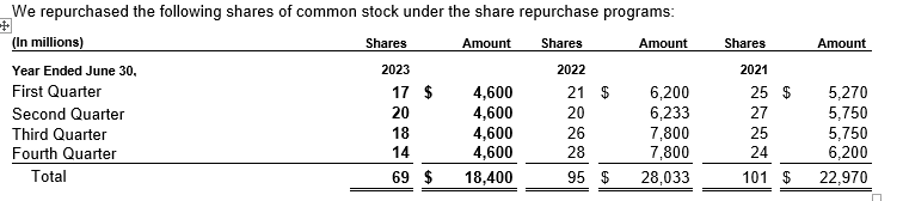
Note: As an additional information Microsoft also discloses in its Annual Report information about its stock performance, share repurchase and dividend payment details as below.
**
9. Board of Directors:
The Annual Report also provided information around the Board of Directors composition as can be seen below in the image:

**
HOW UNDERSTANDING THE ANNUAL REPORT IS IMPORTANT FOR DIFFERENT STAKEHOLDERS OF THE COMPANY?
The sections of the annual report discussed above are useful for different stakeholders of the company as follows:
- Investors: It helps them assess the company’s financial health, profitability, and future growth prospects, enabling informed investment decisions.
- Shareholders: The report provides insights into the company’s performance, dividend policies, and strategic direction, offering transparency on how their investments are managed.
- Employees: For employees, the annual report can highlight the company’s achievements, financial stability, and future plans, giving them confidence in job security and potential career growth.
- Customers and Suppliers: It reassures customers and suppliers of the company’s stability and ongoing success, strengthening trust and long-term business relationships.
- Regulatory Authorities: The report ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, providing a detailed overview of financial and operational activities.
- Analysts and Financial Institutions: It serves as a key document for analyzing the company’s financial performance, competitive position, and industry trends, guiding investment recommendations and decisions.
CONCLUSION
Reading an annual report like Microsoft’s can reveal a wealth of information about the company’s financial health, strategic direction, and operational priorities. By starting with the CEO’s letter, delving into financial statements, exploring the MD&A, and reviewing risk factors and governance, notes to financial statements, and auditors report you gain a complete picture of the company’s performance and future prospects. This approach not only helps in making informed investment decisions but also provides a clearer understanding of the company’s role in the broader business landscape.


