What is the Board of Directors ?
The Board of Directors (BOD) is the governing body elected by shareholders to govern and guide the organisation’s work. The BOD works to maximise the shareholders’ value, manage risk, establish strategies and engage with shareholders to align their and the firm’s interests. The article of incorporation and the corporate laws give the structure and powers to the board of an organisation.
Objectives of Establishing a Board of Directors
The purpose of establishing a Board in the company lies with:
- The BOD puts efforts and makes strategies to maximise and protect the interest of the shareholders. They also ensure transparency and proper communication of financial data with the shareholders.
- A board create policies that help the firm identify, analyse and act to manage and mitigate financial, legal and security risks.
- The BOD engages with stakeholders like shareholders, employees, customers, etc. to ensure their interests and concerns are addressed in the organisation’s decision-making.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Board of Directors
The Board of Directors has the following roles and responsibilities:
- It works on establishing the organisational goals, objectives and strategies.
- The board works on framing the dividend policy and makes dividends distribution decisions.
- The BOD appoints the senior executives and the members of the top management.
- The BOD gives direction to the working of the company.
- The board’s committee works on determining the compensation for the executive staff.
- The board is also directly responsible for the mergers & acquisitions performed by the company.
- The BOD monitors the flow of funds, accounting activities, and the organisation’s budgets.
Types of the Boards
The board can be majorly classified into four types based on their work and roles:
- Executive Board: The role performed by the executive board is to manage the company’s operations. It directs the working of the company towards profitability and growth. The executive board also aligns the company’s work and goals with its values, mission and purpose.
- Advisory Board: The advisory board provide strategic advice, guidance and industry insights to the company. It offers expertise in specific business areas like marketing, finance, technology, industry trends and strategic management.
- Fundraising Board: The fundraising board oversees the responsibility of fund allocation and management in the organisations. Decisions regarding financial resource distribution, budget allocation, evaluation of fundraising proposals, etc are taken by the fundraising board.
- Governing Board: The Governing board is the highest governing body in the organisation.It has the ultimate power to set strategies for the organisation. It also oversees the operations and ensures compliance with ethical standards and bylaws.
Structure of the Board
The board member’s position and responsibilities depend upon the company to determine. But generally, there are five positions on the Board of Directors.
- Chairperson: The highest-ranking member of the board of directors is the Chairperson, sometimes referred to as the Chairman or Chairwoman. They support the board by offering leadership, direction, and counsel, ensuring that organisational objectives are fulfilled and corporate governance principles are respected.
- Vice Chairperson: The vice chair acts as the chairperson’s deputy. They assist the chairman by taking on extra obligations and functions, as well as by doing the chairperson’s tasks when they are not there.
- Secretary: In addition to handling administrative duties, the secretary is in charge of keeping track of board meeting materials, such as minutes, resolutions, and official correspondence.
- Treasurer: The treasurer works with the financial matters of the company. It develops and monitors financial policies, budgets, investment strategies, fundraising initiatives, and risk management practices. The treasurer ensures optimum management of the financial resources of the company.
- Non-Executive Directors: Board members without executive positions are known as non-executive directors. They protect the interests of shareholders by offering governance, monitoring, and strategic direction.
In addition to their main roles, the board can form committees to handle specific aspects of governance, such as audit, compensation, governance, or strategic planning. These committees typically consist of board members, although they may also include outside consultants or subject-matter experts. The main objective of the board’s organisational design is to ensure effective leadership, oversight, and responsibility inside the company.
Board Committees
The board members also serve as members of the committees set up to assist the working of the BOD. Companies majorly function around two to three committees whose members constitute directors or non-executive directors. The number of committees varies from company to company. A few types of committees formed by the board are:
- Compensation Committee: The Compensation Committee, also called the Remuneration Committee, is in charge of managing the salaries paid to executives and staff members. The compensation committee’s main duty is to decide on stock options, bonuses, salary, and other types of pay. The committee works to retain and motivate staff by ensuring that compensation packages reflect the company’s performance, industry norms, and shareholder interests.
- Bylaws Committee: The Bylaw Committee works around the drafting, reviewing and aligning of the rules & regulations of the company to those enforced by the law. The committee also ensures that the organisation is compliant with the legal regulations.
- Audit Committee: The company’s internal control, financial reporting procedures, and other auditing operations are overseen by the Audit Committee. Examining financial statements, assessing the efficacy of internal control, and appointing external auditors are among the main responsibilities. The committee’s primary responsibilities include encouraging regulatory compliance, protecting assets, and guaranteeing accuracy.
- ESG Committee: The Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Committee focuses on sustainability, social responsibility, and corporate governance practices within the organisation. The company focuses on developing ESG strategies and policies. It also monitors and communicates the company’s ESG performance with the shareholders.
- Ad-Hoc Committee: An Ad-Hoc Committee is established for a particular purpose, and once the purpose or task is fulfilled, the committee gets dissolved. The Ad-Hoc Committee is temporary with a defined scope, timeframe and responsibilities.
Board of Directors of Citigroup Inc
Let’s understand the structure of the Board of Directors of Citigroup Inc:
The Citibank was founded in 1812 in New York, as the City Bank of New York.
On March 1, 2021, Jane Fraser held the position of Chief Executive Officer of Citi. Fraser is the first woman to lead a major bank in the US. Her vision for Citi emphasises modernisation, excellence and empathy. Under her leadership, Citi is committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.

Source: https://www.citigroup.com/global/about-us/heritage
Citigroup Inc. aspires to the highest standard of corporate governance and ethical conduct. Citi aims to report accurate financial statements with proper transparency. It pledges to maintain legal and regulatory compliance.
The present Citi’s Board of Directors consists of the following members.

Source: https://www.citigroup.com/global/about-us/leadership
The Board of Directors of Citi aims to offer governance over Citi’s affairs which ultimately benefits its stockholders and to meet the interest of its customers, suppliers, employees and local communities. The candidates for Citi’s board are nominated by the Nomination, Governance & Public Affairs Committee. The shareholders elect the directors in the annual meeting through the voting process. The Nomination, Governance & Public Affairs Committee nominates one board member as the Chairperson of Citi’s board of directors.
As of 2024, the chair of Citigroup Inc. is held by John C. Dugan.
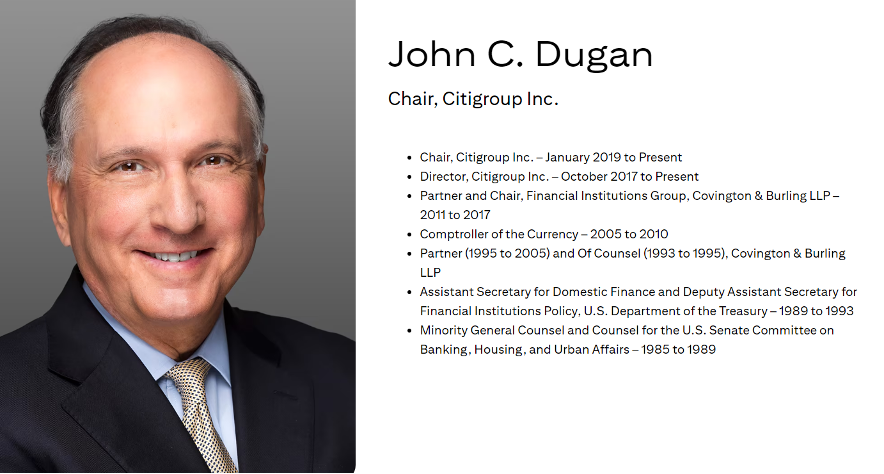
Source: https://www.citigroup.com/global/about-us/leadership
Source: The corporate governance guidelines of Citigroup Inc. as of October 2022. https://www.citigroup.com/rcs/citigpa/storage/public/Corporate%20Governance%20Guidelines%20-%20Oct%2020%202022%20FINAL.pdf
There are six standing committees of the BOD of the Citigroup. They are as follows:
- Executive Committee.
- Audit Committee.
- Risk Management Committee.
- Compensation, Performance Management & Culture Committee.
- Technology Committee.
- Nomination, Governance & Public Affairs Committee.
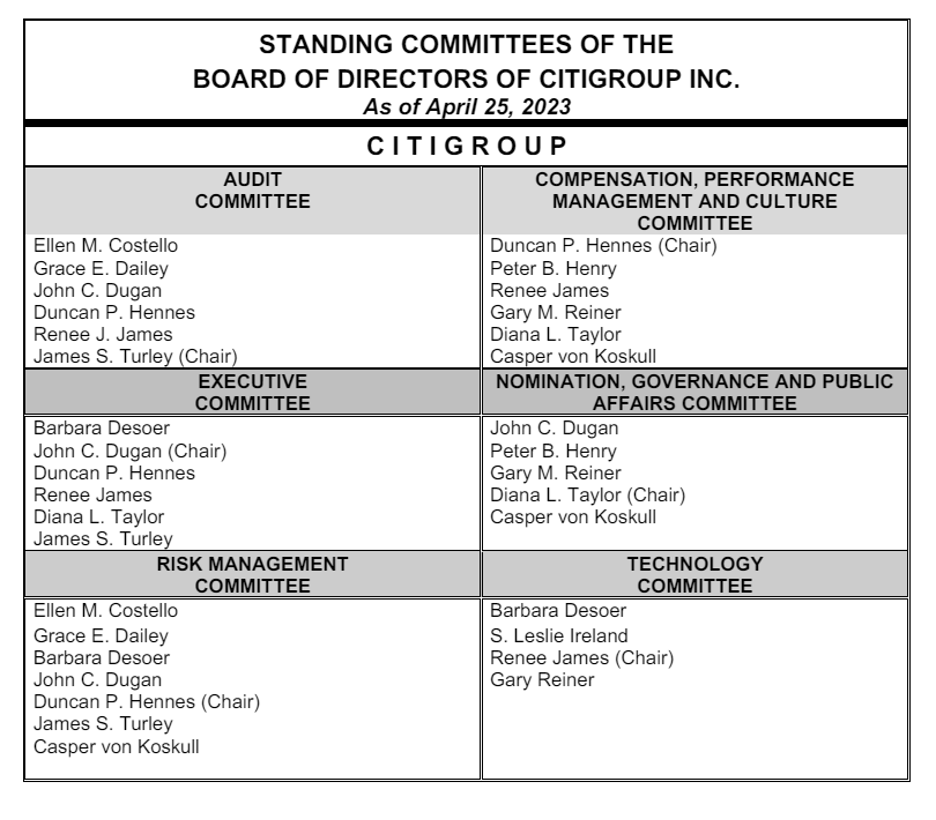
Source: https://www.citigroup.com/rcs/citigpa/akpublic/storage/public/bddircom.pdf
Summing Up
The Board of Directors are the cornerstone of a company’s functioning and corporate governance. With diversity in roles and committees, the board ensures strategic direction, risk management, and maximisation of stakeholder value. Through their leadership and supervision, board members uphold transparency, accountability, and ethical conduct. The Board of Directors protects the shareholder interests, navigates through complexities, fosters innovation, and drives sustainable growth. Empowered by their knowledge and expertise, the board members remain steadfast in their commitment to safeguarding organisational integrity while advancing towards a prosperous future.


