What is Tax Shield?
Tax shield refers to the reduction in the value of the taxable income of an individual or a corporation. Individuals or businesses can claim a tax shield through allowable deductions like interest expense, depreciation and amortisation. Therefore, we can say that a tax shield is a deduction which reduces the overall tax liability of an individual or a firm. Tax shields differ from country to country as the country’s laws classify items eligible for deductions.
A few common types of deductions are:
- Depreciation: Depreciation is a non-cash expense which leads to a reduction in the monetary value of an asset. It is the wear and tear of assets due to usage. A company records depreciation in the income statement before the calculation of taxes. The recording of depreciation reduces the net income earned by a company during a financial year. As a result, the tax liability payable by the firm decreases.
- Interest: Interest expenses refer to the cost incurred by a company for borrowing funds from external parties like banks, financial institutions, etc. Companies record interest expense in the income statement before recording tax liability.
- Amortisation: Amortisation refers to the expense charged on the value of intangible assets. It is the accounting process where intangible assets like goodwill, patents, trademarks, etc, are written off over a period.
Formula of Tax Shield:
| Tax Shield | = Deduction Amount * Tax Rate |
- Deduction Amount: It refers to the amount of allowable deduction which leads to tax reduction. Common examples of deductible amounts are interest, depreciation, amortisation, etc.
- Tax Rate: The tax rate is the percentage of tax imposed on the income of individuals or corporations by the government of a country.
Real Life Example of Tax Shield:
Let’s understand the calculation of the Tax Shield of GE for 2023:
Calculation of Tax Shield of GE for 2023:
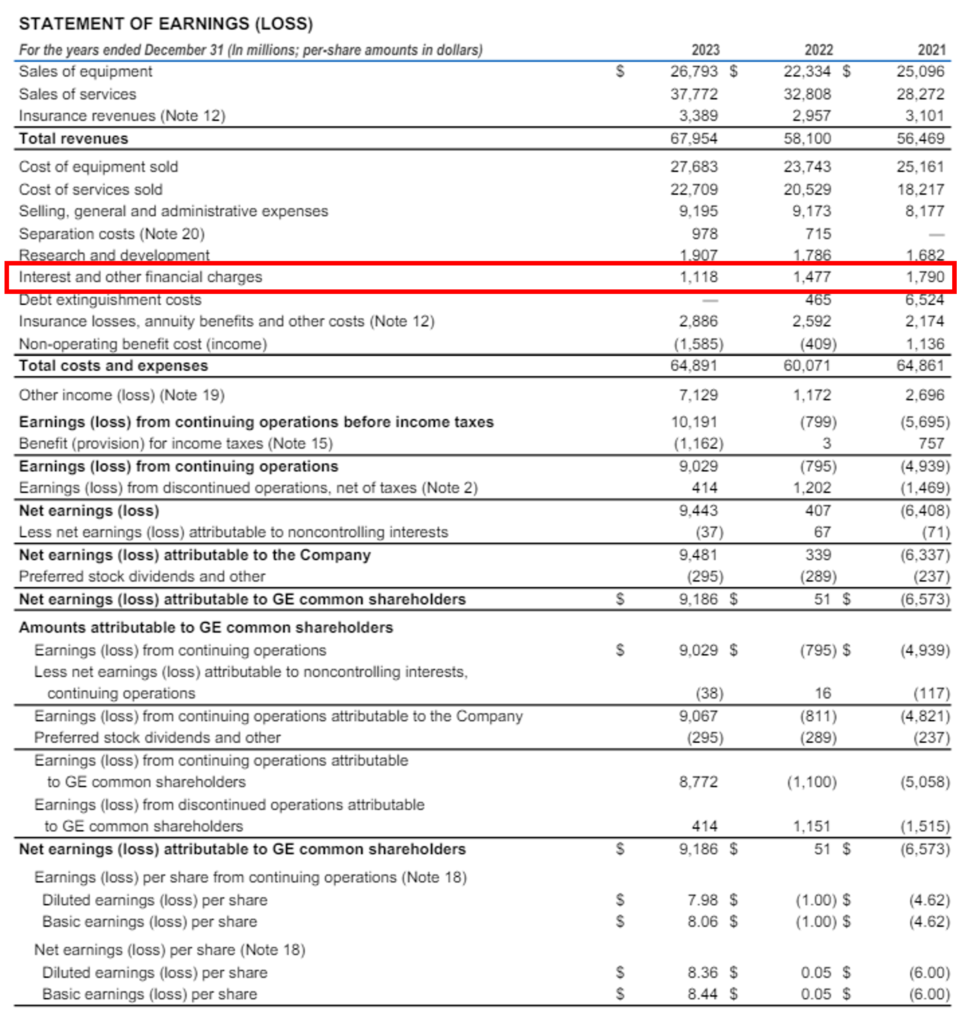
| Interest Expense for FY 2023 | = $1,118 million |
Source: https://www.ge.com/sites/default/files/ge_ar23_10-k.pdf
Note: The value of depreciation and amortisation is taken from the table recorded in Note 25: Operating Segment on page: 80 of GE’s 2023 10-K report.
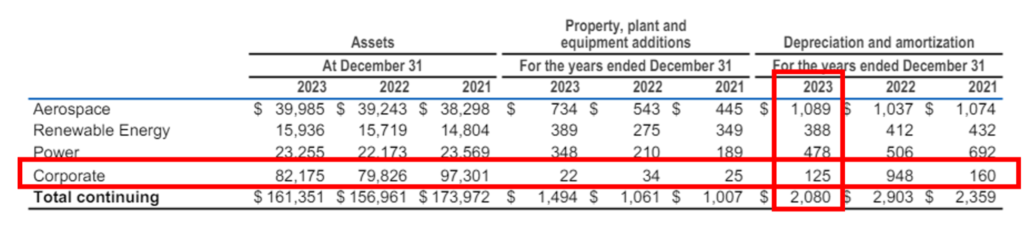
| Depreciation & Amortisation | = $2,080 million |

Note: For the Tax Shield calculation, we have taken the effective tax rate of GE for 2023. The above table is provided on page: 14 of the 10-K report.
| Tax Rate | = 11.4% |
| Tax Shield | = (Interest Expense + Depreciation & amortisation) * Tax Rate |
| = (1,118 + 2,080) * 11.4% | |
| = 3,198 * 11.4% | |
| Tax Shield | = $364.5 million |
The Tax Shield of GE for 2023 was equal to $364.5 million. We can also calculate the value of the tax shield by adding the figures of interest tax shield and depreciation tax shield.
Strategies Used by Corporations
Companies and businesses use tax shields in two strategic ways:
- To determine the optimum capital structure of the business: Under capital structure strategy, companies opt for a capital structure that helps them minimise the cost of capital plus tax liability. Companies can either issue shares to raise funds or take debt. For capital structure decisions, many companies try to take advantage of interest expense as it is a tax-deductible expense, while the dividend is not a tax-deductible expense. Based on this perspective, often corporates opt for debt funding as it becomes a cheaper alternative.
- Acceleration of depreciation by the companies: In this tax shield strategy, the companies accelerate the recording of deprecation to its highest value in the early stages to minimise the taxes. Companies try to maximise their depreciation expense to reduce the tax liability.
Types of Tax Shields
- Interest Tax Shield: Interest tax shield refers to the tax savings resulting from the tax-deductible nature of interest expense. When a company includes debt in its capital structure, the interest expense is the cost of raising debt capital. This interest expense is recorded in the company’s income statement under non-operating expenses and reduces the company’s net income. Interest tax shield offsets the cost of debt, which is why companies prefer taking more debt over equity.
Formula of Interest Tax Shield:
| Interest Tax Shield | = Interest Expense * Tax Rate |
Calculation of Interest Tax Shield of GE for 2023:
| Interest Expense | = $1,118 million |
| Tax Rate | = 11.4% |
| Interest Tax Shield | = Interest Expense * Tax Rate |
| = 1,118 * 11.4% | |
| Interest Tax Shield | = $127.4 million |
The interest tax shield of GE for 2023 was $127.4 million.
- Deprecation Tax Shield: Depreciation Tax Shield refers to the tax shielding benefit caused by recording depreciation expense. The depreciation expense is a line item of the income statement, which reduces the company’s Earnings Before Tax (EBT) and total tax liability.
Formula of Depreciation Tax Shield:
| Depreciation Tax Shield | = Depreciation Expense * Tax Rate |
Calculation of Depreciation Tax Shield of GE for 2023:
| Depreciation & Amortisation | = $2,080 million |
| Tax Rate | = 11.4% |
| Depreciation Tax Shield | = Depreciation Expense * Tax Rate |
| = 2,080 * 11.4% | |
| Depreciation Tax Shield | = $237.1 million |
The depreciation tax shield of GE for 2023 was $237.1 million.
Conclusion
The tax shield serves as a vital tool for individuals and corporations alike, reducing taxable income and tax liabilities through allowable deductions such as interest, depreciation, and amortisation. These deductions vary based on country-specific regulations, enabling businesses to strategically optimise their capital structure and minimise costs while maximising shareholder value. By leveraging tax shields, companies can strategically manage their finances, accelerate depreciation, and capitalise on interest expense deductions to enhance overall profitability. This strategic utilisation of tax shields underscores their significance as a key component of effective financial management and tax planning strategies.


