What is ESG?
The abbreviation ESG stands for Environment, Social and Governance. The Environmental, Social and Governance framework evaluates an organisation’s performance and practices on sustainability and ethical issues.
Three Pillars of ESG
- The Environmental criteria examine the influence of a company’s business operations on its surroundings. It measures how the business manages its operational and product’s impact on the environment.
- Under Social criteria, the business focuses on building and maintaining relationships with different stakeholders. The company also strives to create value for stakeholders, including suppliers, employees, government, customers, etc.
- The Governance factor of ESG works on management philosophies, policies, practices and values. The governance criteria are wholly associated with how the company is led and managed.
The perspective of ESG is not limited to the values of the companies regarding their environmental, social and economic domains. But circles around how a company creates and sustains its long-term values in the dynamic world. This long-term sustainability of values includes risk management and opportunities realisation that arise due to these changes.
Factors that promote ESG
In the corporate world, three elementary factors drive the growth and requirement of ESG. They are materiality, transparency and regulation.
- Materiality focuses on how investors weigh ESG with the risk and return of a business. Recognition of these relations leads to the long-term success of businesses. To understand materiality, businesses perform materiality analysis. It is a process which identifies important ESG issues and stakeholders which can help sustain the long-term growth of a business.
- Materiality leads to the need for transparency. Investors and clients demand greater transparency on how the company invests their money.
- Regulation is the final factor that led to ESG as a mainstream business concept. Regulations at national and international levels help businesses to check that they are not violating any environmental, social or government norms.
Importance of ESG
The importance of ESG is reflected in the company’s long-term growth as it positively impacts foundational business issues like climate change, pollution, labour management, etc.
- Risk Management – ESG criteria help businesses forecast and prepare for numerous risks like evolving regulations, labour availability, scarcity of resources, etc.
- Corporate Image – How corporates present their ESG perspective to investors and the public shows how aware the business is of its potential risks and opportunities. Making it easier for corporates to achieve their goals and sustain long-term growth.
- Opportunity Management – The dynamic nature of the business environment leads to constant changes in the demand and supply of goods and services. Through ESG assessment, businesses can capitalise on such opportunities and prepare for possible threats.
- Example: There is a growing consumer preference for products and services from companies that are socially and environmentally responsible. Thus, businesses can capitalise on this opportunity by producing vegan, eco-friendly and cruelty-free goods.
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are bringing strict guidelines and initiatives for environmental protection, social responsibility, and corporate governance. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals is one of the major initiatives.
- Culture and Value Formation – Integrating ESG factors and regulations in business operations helps shape the attitudes, behaviours and skills of stakeholders and human resources. ESG criteria inculcate values like environmental protection, pollution control, wise use of non-renewable resources, etc. Therefore, it helps create a culture that encourages and supports ESG values.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage: ESG can drive innovation, opening up new markets and opportunities. By capitalising on such opportunities companies can gain a significant competitive advantage over peer companies. Also if businesses adopt sustainable business practices, it can be a significant differentiator in a crowded marketplace.
Factors under ESG
Under the ESG framework, a company evaluates numerous factors under environmental, social and governance heads. Here are some fundamental factors typically assessed under each category:
Environmental Factors:
- Climate Change.
- Optimum use of natural resources.
- Pollution and waste management.
- Compliance with Environmental Laws and Guidelines.
- Preservation and Service towards Biodiversity and Ecosystem.
Social Factors:
- Adoption of healthy & safe Labour Practices.
- Adoption of diversity and inclusion policies within the workforce, gender and racial equality.
- Training and development of human capital.
- Customer welfare by offering safe products and through fair market practices.
Governance Factors:
- Adoption of ethical business practices and anti-corruption measures.
- Ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory guidelines is imperative.
- Investment strategies and fund allocation must be transparent for investors and regulators.
Real-Life Example of ESG – Nvidia
Every year NVIDIA publishes a corporate responsibility report. Therefore, by taking it as a reference we will try to understand the ESG strategies of NVIDIA for 2023.
Some key highlights from NVIDIA’s Corporate Responsibility Report for Fiscal Year 2023 include:
- Development of technologies that contribute positively to society, with a focus on responsible development and use of AI.
- Commitment to societal innovation, particularly in the healthcare sector, by harnessing the power of AI and high-performance computing to advance personalised medicine, enhance quality of care, and drive breakthroughs in biomedical research.
- Commitment to sustainability reporting frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) to ensure transparency and accountability in reporting corporate responsibility efforts.
- Alignment of social impact activities with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals to contribute to global sustainability and development objectives.
Business Practices of NVIDIA
NVIDIA’s business practices encompass a range of initiatives and strategies that reflect the company’s commitment to ethical conduct, sustainability, innovation, and stakeholder engagement. Some core aspects of NVIDIA’s business practices include:
- Code of Conduct and Human Rights: NVIDIA requires all employees to complete training on its code of conduct, which includes guidelines on respecting human rights. The company provides avenues for employees to report concerns about human rights violations confidentially and ensures prompt investigation and action to address any issues.
- Sustainability and Environmental Stewardship: NVIDIA is dedicated to sustainability and environmental stewardship by implementing energy-efficient practices, managing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting sustainable operations across its product lifecycle. The company focuses on reducing its environmental impact and supporting climate action through various initiatives.
- Innovation and Technology Development: NVIDIA is known for its innovation in accelerated computing, AI, deep learning, and other cutting-edge technologies. The company’s products and services are designed to drive advancements in various industries and contribute to societal innovation.
- Corporate Responsibility and Stakeholder Engagement: NVIDIA actively engages with stakeholders and communities to address social and environmental challenges. The company’s corporate responsibility efforts focus on diversity and inclusion, supply chain management, product impact, and sustainability reporting frameworks.
- Employee Benefits and Well-being: NVIDIA offers comprehensive benefits programs to support the well-being of its employees and their families. This includes competitive wages, flexible work hours, mental and physical well-being programs, parental leave, tuition reimbursement, and professional development opportunities.
- Talent Attraction and Recruitment: NVIDIA prioritises talent attraction and recruitment by partnering with educational institutions, professional organisations, and industry conferences to diversify its candidate pipeline. The company focuses on creating opportunities for global talent and supporting underrepresented communities in the recruitment process.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: NVIDIA maintains robust information security and cybersecurity practices to protect confidential information and secure its products and services. The company continuously evolves its strategies to address emerging security risks and complies with data privacy regulations.
NVIDIA and Sustainability
NVIDIA has implemented several sustainability efforts to reduce its environmental impact and promote climate action. Some of these initiatives include:
- Energy Efficiency: NVIDIA focuses on improving the energy efficiency and performance of its products. For example, the company has developed liquid-cooled GPUs that consume less power and rack space compared to traditional air-cooled servers, leading to energy savings.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions Management: NVIDIA assesses its carbon footprint across the product lifecycle and evaluates climate risks, including regulatory and market impacts. The company is committed to managing its greenhouse gas emissions and has set a goal to purchase or generate enough renewable energy to match 100% of its global electricity usage for offices and data centres by the end of the fiscal year ending January 26, 2025.
- Sustainable Practices: NVIDIA implements energy and environmental management systems, certifications, policies, procedures, and programs to promote sustainability. The company also focuses on water conservation, waste management, and efforts around product packaging, transport, and end-of-life management.
- Climate Change Mitigation: NVIDIA leverages its technology to support climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts.
NVIDIA on People, Diversity & Inclusion:
In 2023, NVIDIA demonstrates its commitment to diversity and inclusion in the workplace through various initiatives and practices, including:
- Talent Attraction and Recruitment: NVIDIA actively recruits diverse talent by partnering with higher education institutions, professional organisations, and industry conferences. The company encourages employee referrals and has dedicated recruiters to assist women and underrepresented communities through the recruitment process.
- Inclusive Work Environment: NVIDIA fosters an inclusive work environment that supports all employees, regardless of gender, age, race, ethnicity, or disability. The company prioritise creating a culture where diverse teams can thrive and contribute to innovation.
- Employee Engagement: NVIDIA values employee feedback and engagement, conducting frequent surveys to measure employee satisfaction, engagement levels, and culture. This robust approach allows the company to address specific areas of improvement and respond quickly to employee needs and concerns.
- Professional Development and Training: NVIDIA invests in professional and leadership development programs to support the growth and advancement of all employees. The company provides opportunities for skill-building, career advancement, and continuous learning to ensure a diverse and inclusive workforce.
- Health and Safety Policies: NVIDIA prioritises the health and safety of its employees by implementing policies, programs, and performance measures to maintain a safe work environment. The company is committed to ensuring the well-being of all employees.
Top 25 Global ESG Scorers in 2023
The following graph shows the list of 25 companies that scored highest in ESG ranking in 2023:
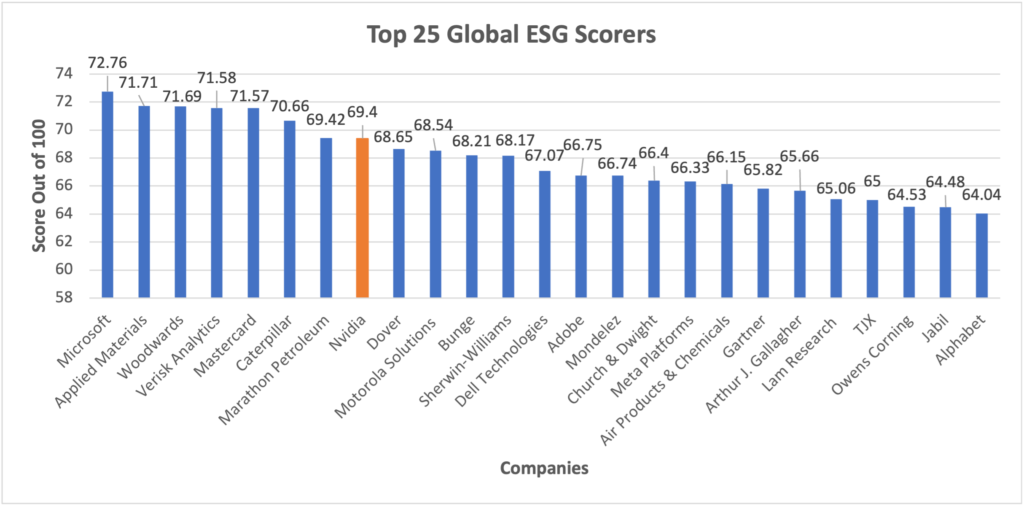
Microsoft holds the first position by scoring 72.76 out of 100. Followed by Applied Materials and Woodwards with 71.71 and 71.69 points respectively.
In 2023, NVIDIA scored 69.4 points and holds the 8th position in the top 25 global ESG scorers.
Difference Between CSR and ESG
The concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) focuses on philanthropy, community involvement and ethical corporate practices. ESG is a more holistic concept which involves environmental, social and governance factors of a business.
CSR is considered a separate aspect from core business strategies. However, corporates integrate ESG into core business functioning. The ESG strategies are used by companies to assess risk and identify opportunities in the ever-changing business environment. CSR focuses on a specific stakeholder group, including environmental NGOs, local community, volunteerism, etc. But EGS engage many stakeholders like investors, customers, suppliers, regulators, employees, local communities, etc.
Thus, we can say that ESG is a broader concept which ultimately evolved by improving corporate social responsibility.
Summing Up
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) emerges as a comprehensive framework crucial for businesses navigating the dynamic landscape of sustainability and ethical responsibility. It surpasses mere corporate social responsibility by integrating environmental impact, social engagement, and governance practices into the core organisational strategies.
Through ESG, companies fortify their long-term viability, anticipate and manage various risks, and enhance their corporate reputation.ESG thus emerges as a roadmap for companies steering through the complex and dynamic business environment.


